How many calories per mile cycling? This question has intrigued cyclists of all levels, from beginners to seasoned veterans. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the factors that influence calorie expenditure during cycling, provide data on the average calorie burn rate, and explore methods for tracking and maximizing calorie burn while cycling.
Whether you’re looking to improve your fitness, manage your weight, or simply enjoy the health benefits of cycling, understanding how many calories you burn per mile can help you tailor your workouts and achieve your goals.
Energy Expenditure while Cycling
Cycling is a fantastic cardio exercise that offers numerous health benefits. One crucial aspect of cycling is understanding the energy expenditure associated with it. Calorie burn during cycling depends on several factors, including speed, terrain, and body weight.
Factors Influencing Calorie Expenditure
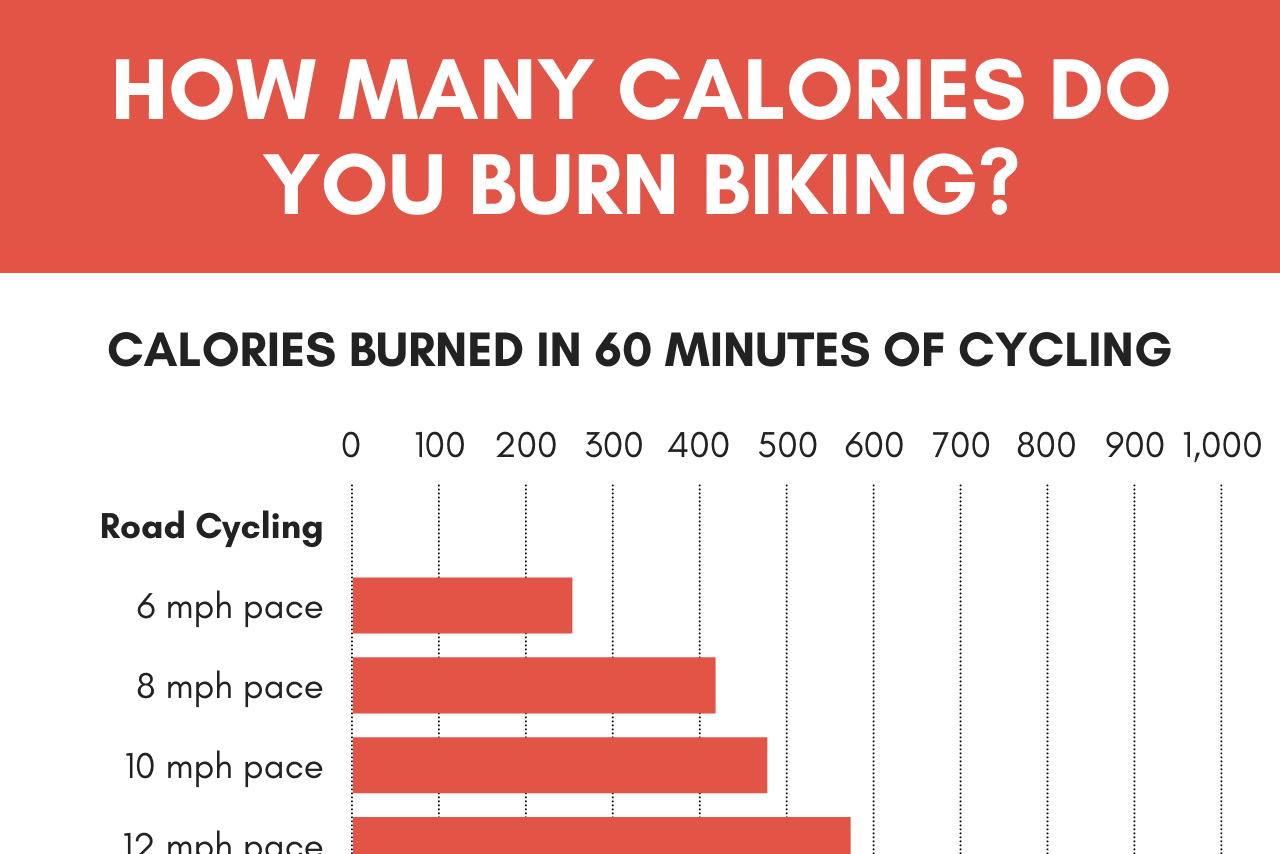
- Speed:Cycling at higher speeds requires more energy output, resulting in increased calorie burn.
- Terrain:Riding on hilly or uneven terrain requires more effort, leading to higher calorie expenditure compared to flat surfaces.
- Body Weight:Heavier individuals generally burn more calories while cycling due to the increased resistance they encounter.
Estimating Calorie Burn
To estimate the number of calories burned while cycling, you can use the following formula:
Calories Burned = (MET x Body Weight in kg x Time in hours)
Where MET is the metabolic equivalent of task, which represents the energy cost of an activity relative to resting metabolism. For moderate-intensity cycling, MET is approximately 6.
For example, a 70 kg person cycling for one hour at moderate intensity would burn approximately (6 x 70 x 1) = 420 calories.
Calorie Burn Rate
Cycling is an excellent cardiovascular exercise that burns a significant number of calories. The rate at which you burn calories while cycling depends on several factors, including the intensity of your workout, the duration of your ride, your fitness level, and your individual body composition.
Average Calorie Burn Rate, How many calories per mile cycling
On average, a person weighing 155 pounds (70 kilograms) can expect to burn the following number of calories per mile while cycling:
Light intensity
60-70 calories per mile
Moderate intensity
70-100 calories per mile
If you’re looking to improve your flexibility, foam rolling is a great option. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to foam roll your inner thighs, helping you reduce muscle soreness and increase your range of motion.
Vigorous intensity
100-150 calories per mileThese estimates are just averages, and your actual calorie burn rate may vary depending on your individual circumstances.
Factors Affecting Calorie Burn Rate
Intensity:The intensity of your workout is the most significant factor affecting your calorie burn rate. The harder you work, the more calories you’ll burn. Duration:The duration of your ride also plays a role in how many calories you burn. The longer you ride, the more calories you’ll burn.
Fitness level:Your fitness level also affects your calorie burn rate. The fitter you are, the more efficiently you’ll be able to burn calories. Body composition:Your body composition, specifically your muscle mass, also affects your calorie burn rate. The more muscle mass you have, the more calories you’ll burn.It’s important to note that these are just general guidelines.
Your actual calorie burn rate may vary depending on your individual circumstances. If you’re unsure how many calories you’re burning while cycling, you can use a calorie-tracking app or consult with a fitness professional.
Calorie Tracking and Monitoring
Tracking calorie expenditure during cycling is essential for weight management and fitness goals. Several methods are available to accurately monitor calorie burn, including:
- Fitness Trackers:Wearable devices like smartwatches or fitness bands monitor heart rate, steps taken, and distance traveled, providing an estimate of calorie expenditure.
- Heart Rate Monitors:Chest straps or wrist-worn devices measure heart rate, which correlates with calorie burn. Higher heart rates indicate increased calorie expenditure.
- Calorie-Tracking Apps:Smartphone apps allow users to log cycling activities and input personal data to estimate calorie burn based on factors like distance, duration, and intensity.
Accurate calorie tracking helps cyclists:
- Set realistic calorie goals for weight loss or maintenance.
- Monitor progress towards fitness objectives.
- Identify areas for improvement in training or nutrition.
- Prevent over or under-eating, leading to better overall health and well-being.
Nutrition and Calorie Intake
Nutrition plays a vital role in supporting cycling performance and calorie expenditure. A balanced diet provides the body with the necessary fuel to sustain high-intensity cycling and aid in recovery.
Balancing calorie intake with cycling intensity and duration is crucial. Consuming too few calories can lead to fatigue and decreased performance, while excessive calorie intake can result in weight gain and impaired performance.
Macronutrient Considerations
Macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, contribute to different aspects of cycling performance.
- Carbohydrates:Provide the primary fuel for cycling, especially during high-intensity efforts.
- Proteins:Essential for muscle repair and growth, aiding in recovery from cycling.
- Fats:Provide sustained energy and support hormone production, crucial for long-duration cycling.
Hydration
Hydration is equally important. Dehydration can impair performance and lead to cramps and fatigue.
- Drink plenty of fluids before, during, and after cycling.
- Consider sports drinks to replenish electrolytes lost through sweat.
Sample Meal Plan
A sample meal plan for a cyclist might include:
- Breakfast:Oatmeal with fruit and nuts, providing carbohydrates and protein.
- Lunch:Salad with grilled chicken, quinoa, and vegetables, offering a balance of carbohydrates, protein, and fiber.
- Dinner:Pasta with lean meat sauce and steamed broccoli, providing sustained energy and nutrients for recovery.
Health Benefits of Cycling
Regular cycling offers numerous health benefits, contributing to improved overall well-being. These benefits are primarily attributed to the calorie expenditure associated with cycling, which plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy weight and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Cardiovascular Health
Cycling is an excellent cardiovascular exercise that strengthens the heart and improves blood circulation. The increased heart rate during cycling helps to pump more oxygen-rich blood throughout the body, delivering essential nutrients to cells and tissues. This improved circulation reduces the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions.
Weight Management
Cycling is an effective way to burn calories and manage weight. The amount of calories burned during cycling depends on factors such as the intensity and duration of the ride, as well as the individual’s weight and fitness level. Regular cycling can help to create a calorie deficit, promoting weight loss and preventing weight gain.
Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
Cycling has been linked to a reduced risk of developing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer, and arthritis. The calorie expenditure associated with cycling helps to maintain a healthy weight, which is a significant risk factor for these diseases.
Additionally, cycling improves insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, and strengthens muscles and joints, which can help prevent arthritis.
Cycling for Weight Loss
Cycling is an excellent form of exercise for weight loss, as it burns a significant number of calories. The number of calories burned per mile depends on several factors, including the intensity of the ride, the duration of the ride, and the rider’s weight.
The following table provides an estimate of the potential calorie burn per mile cycling at different intensities and durations:
| Intensity | Duration (minutes) | Calories Burned per Mile |
|---|---|---|
| Light | 30 | 100-150 |
| Moderate | 30 | 150-200 |
| Vigorous | 30 | 200-250 |
| Light | 60 | 150-200 |
| Moderate | 60 | 200-250 |
| Vigorous | 60 | 250-300 |
Here are some examples of cycling workouts designed for weight loss and calorie burn:
- Interval training:This type of workout involves alternating between periods of high-intensity cycling and periods of rest or low-intensity cycling. Interval training is a very effective way to burn calories and improve cardiovascular fitness.
- Hill repeats:This type of workout involves cycling up a hill at a high intensity and then recovering on the way down. Hill repeats are a great way to build strength and burn calories.
- Long, steady rides:This type of workout involves cycling at a moderate intensity for an extended period of time. Long, steady rides are a great way to burn calories and improve endurance.
Calorie Burn Comparison
Cycling is a fantastic exercise for burning calories and improving cardiovascular health. However, how does it compare to other forms of exercise in terms of calorie expenditure?
Several factors influence calorie burn during exercise, including intensity, duration, and body weight. Let’s explore how cycling stacks up against other popular exercises.
If you’re an avid motorcyclist, you’ll want to make sure your helmet is up to par. Check out this article to learn how often you should replace your helmet and why it’s crucial for your safety.
Running
Running is another excellent cardio exercise that burns a significant number of calories. The calorie expenditure for running is generally higher than cycling at the same intensity and duration.
This is because running engages more muscle groups, including the legs, core, and arms. The impact of running also contributes to increased energy expenditure.
Swimming
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that is easy on the joints. It is also a great way to burn calories, although the rate may be slightly lower than cycling or running.
The water provides resistance, which helps to engage multiple muscle groups. However, the buoyancy of water reduces the overall impact and energy expenditure compared to land-based exercises.
Strength Training
Strength training, such as weightlifting or resistance exercises, primarily focuses on building muscle mass. While it may not burn as many calories as cardio exercises during the workout, it can increase metabolism and calorie burn over time.
By building muscle, strength training helps to increase the body’s resting metabolic rate, meaning you burn more calories even at rest.
Tips for Maximizing Calorie Burn: How Many Calories Per Mile Cycling
Optimizing calorie burn while cycling requires proper technique, interval training, and hill climbing. These techniques enhance calorie expenditure by engaging different muscle groups, increasing intensity, and challenging the cardiovascular system.
Understanding the physiological mechanisms behind these techniques is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness.
Proper Technique
- Maintain a comfortable and efficient cycling posture, with the saddle height adjusted to allow for a slight bend in the knees at the bottom of the pedal stroke.
- Engage your core muscles to stabilize your body and prevent excessive movement, which can waste energy.
- Use a high cadence (80-100 revolutions per minute) to increase muscle activation and calorie burn.
Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating periods of high-intensity cycling with rest or low-intensity cycling.
- High-intensity intervals push your body to its limits, increasing oxygen consumption and calorie expenditure.
- Rest or low-intensity intervals allow for recovery and replenishment of energy stores, preparing you for the next high-intensity interval.
- The duration and intensity of the intervals can be adjusted based on your fitness level and goals.
Hill Climbing
Hill climbing is an effective way to challenge your cardiovascular system and burn calories.
- The increased resistance requires your body to work harder, engaging more muscle groups and increasing calorie expenditure.
- Tackling hills at a steady pace helps maintain a high heart rate and calorie burn rate.
- Incorporating hill climbs into your cycling routine can significantly boost your overall calorie burn.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, cycling is an excellent form of exercise for burning calories, improving cardiovascular health, and supporting weight management. By understanding the factors that influence calorie expenditure and incorporating our tips for maximizing calorie burn, you can optimize your cycling workouts and achieve your fitness and health goals.
Answers to Common Questions
How can I track my calorie expenditure while cycling?
You can use fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, or calorie-tracking apps to monitor your calorie burn during cycling.
How does my fitness level affect my calorie burn rate?
Fitter individuals tend to burn more calories per mile cycling compared to beginners due to increased muscle mass and efficiency.
What are some tips for maximizing calorie burn while cycling?
Proper technique, interval training, and hill climbing can help you burn more calories while cycling.
