How many ounces of 2 cycle oil per gallon? This is a question that every small engine owner should know the answer to. Using the right ratio of oil to gasoline is essential for keeping your engine running smoothly and efficiently.
Too much oil can cause the engine to smoke and foul the spark plugs, while too little oil can lead to engine damage.
In this guide, we’ll tell you everything you need to know about mixing 2 cycle oil with gasoline. We’ll cover the standard ratio, how to convert ounces to gallons, and the steps on how to mix the oil and gasoline together.
We’ll also discuss premixed fuel options and safety considerations.
Ratio of 2-Cycle Oil to Gasoline
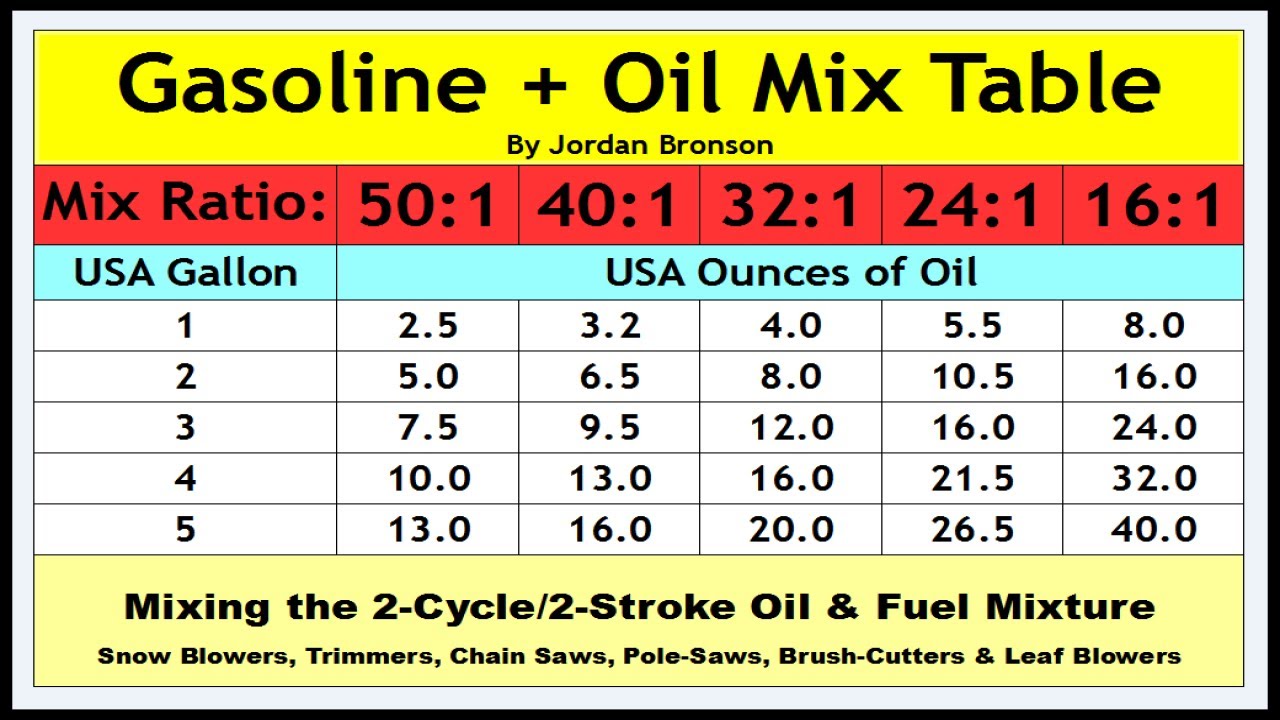
When using 2-cycle engines, it is crucial to maintain the correct ratio of oil to gasoline. The standard ratio for small engines is 50:1, which means 50 parts gasoline to 1 part oil.
Did you know that the cost of a flomarching subscription can vary depending on the package you choose? It’s always a good idea to research different options to find the best deal. On a different note, have you ever wondered how to clean a platypus bladder?
It’s a surprisingly simple process that only requires a few household items. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get the job done.
Maintaining the correct ratio is essential for the proper functioning and longevity of the engine. Too much oil can cause spark plug fouling, excessive smoke, and engine damage. Conversely, too little oil can lead to insufficient lubrication, resulting in premature wear and potential engine seizure.
Importance of Maintaining the Correct Ratio
Using the correct ratio of oil to gasoline ensures optimal performance and protection for your 2-cycle engine. Here’s why it’s important:
- Proper Lubrication:Oil provides lubrication for the moving parts within the engine, reducing friction and wear.
- Cooling:Oil helps dissipate heat generated by the engine, preventing overheating and damage.
- Fuel Mixture:The oil-gasoline mixture creates a combustible fuel that powers the engine.
- Engine Protection:The correct ratio of oil protects the engine from premature wear, corrosion, and damage.
Consequences of Using Too Much or Too Little Oil
Deviating from the recommended oil-to-gasoline ratio can have adverse effects on the engine:
- Too Much Oil:
- Spark plug fouling
- Excessive smoke
- Engine damage due to carbon buildup
- Too Little Oil:
- Insufficient lubrication
- Premature wear
- Potential engine seizure
Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific engine you are using to ensure the correct oil-to-gasoline ratio.
Measurement Conversions
Understanding the relationship between ounces and gallons is crucial when measuring 2-cycle oil for gasoline mixtures. This table provides conversions for common ounce measurements to their gallon equivalents, simplifying the process of preparing the correct ratio.
Conversion Table
| Ounces (oz) | Gallons (gal) |
|---|---|
| 8 | 0.5 |
| 16 | 1 |
| 32 | 2 |
| 64 | 4 |
| 128 | 8 |
To manually convert ounces to gallons, divide the number of ounces by 128. For example, to convert 32 ounces to gallons: 32 oz ÷ 128 oz/gal = 0.25 gal.
Mixing s
Mixing 2-cycle oil with gasoline is essential for the proper functioning of 2-cycle engines. Follow these s carefully to ensure a well-mixed fuel mixture.
Before mixing, gather the necessary tools and containers: a clean, graduated measuring container, a funnel, and a suitable mixing container. Wear gloves and safety glasses for protection.
If you’re looking for a thorough guide on how to clean a platypus bladder, this article has got you covered. It provides step-by-step instructions to ensure your bladder stays clean and hygienic. Now, switching gears to a different topic, if you’re interested in subscribing to FloMarching, here’s a resource that provides pricing information and subscription options.
It’s important to weigh the costs and benefits before making a decision.
Measuring and Mixing
- Determine the required oil-to-gasoline ratio for your engine. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations or consult a reliable source.
- Measure the required amount of 2-cycle oil using the graduated measuring container.
- Pour the measured oil into the mixing container.
- Add a small amount of gasoline to the mixing container and stir thoroughly to dissolve the oil.
- Gradually add the remaining gasoline while stirring continuously to ensure a uniform mixture.
- Once all the gasoline has been added, continue stirring for a few more minutes to ensure complete mixing.
Safety Precautions
- Always mix in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes.
- Do not smoke or have open flames near the mixing area.
- Store the mixed fuel in an approved container and keep it away from children and pets.
Premixed Fuel Options
Premixed fuel options offer a convenient and reliable way to ensure the proper ratio of 2-cycle oil to gasoline in your engine. These pre-mixed fuels are specifically designed for use in 2-cycle engines and eliminate the need for manual mixing, reducing the risk of incorrect ratios.
Premixed fuel options come in a variety of formulations, each tailored to specific engine requirements. They typically consist of a blend of high-quality gasoline and the appropriate amount of 2-cycle oil, ensuring optimal performance and lubrication.
Advantages of Premixed Fuel
- Convenience:Premixed fuel eliminates the hassle of manual mixing, saving time and effort.
- Accuracy:Premixed fuel guarantees the correct ratio of oil to gasoline, ensuring optimal engine performance and protection.
- Reduced Risk of Errors:Premixed fuel eliminates the risk of incorrect mixing ratios, which can lead to engine damage.
- Enhanced Engine Life:Properly mixed fuel ensures adequate lubrication, reducing wear and tear on engine components, extending engine life.
Disadvantages of Premixed Fuel
- Cost:Premixed fuel can be more expensive than mixing your own fuel, as it includes the cost of both gasoline and oil.
- Limited Availability:Premixed fuel may not be readily available in all locations, especially in remote areas.
- Storage Concerns:Premixed fuel has a shorter shelf life than pure gasoline, so it’s important to use it promptly.
Examples of Premixed Fuel Products
- Echo Power Blend:A premixed fuel designed for Echo 2-cycle engines, providing optimal performance and protection.
- Husqvarna XP Power:A premixed fuel formulated for Husqvarna 2-cycle engines, ensuring maximum power and durability.
- Stihl Motomix:A high-performance premixed fuel engineered for Stihl 2-cycle engines, offering excellent lubrication and protection.
Safety Considerations
When handling 2-cycle oil, safety precautions are paramount to minimize potential hazards and ensure a safe environment.
2-cycle oil, composed of various chemical compounds, can pose risks if not handled appropriately. Inhalation of oil vapors or prolonged skin contact can cause irritation or allergic reactions in some individuals. Moreover, improper storage or disposal practices can lead to environmental contamination.
Hazards and Precautionary Measures
- Inhalation:Avoid inhaling oil vapors. If exposed to excessive fumes, move to a well-ventilated area and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Skin Contact:Prolonged or repeated skin contact with 2-cycle oil can cause irritation or allergic reactions. Wear protective gloves when handling oil and wash hands thoroughly after use.
- Eye Contact:In case of eye contact, flush eyes immediately with clean water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention.
Proper Storage and Disposal
- Storage:Store 2-cycle oil in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. Keep containers tightly closed to prevent spills and leaks.
- Disposal:Never pour used 2-cycle oil into drains, waterways, or on the ground. Dispose of used oil responsibly by taking it to a designated oil recycling center or following local regulations.
Engine Compatibility
When selecting 2-cycle oil, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with your specific engine. Different oils are formulated with varying properties, such as viscosity, detergent additives, and anti-wear agents, which may not be suitable for all engines.
Engine Manufacturer Recommendations
The best approach is to consult your engine manufacturer’s specifications. They will provide specific recommendations for the type and ratio of 2-cycle oil to use. This information is typically found in the owner’s manual or on the engine itself.
Factors to Consider
Consider the following factors when selecting 2-cycle oil for your engine:
- Engine Type:Different engine types, such as air-cooled or water-cooled, may require different oil formulations.
- Operating Conditions:Extreme temperatures or high-performance applications may necessitate specialized oils.
- Oil Viscosity:The oil’s viscosity should match the manufacturer’s recommendations to ensure proper lubrication and performance.
- Detergent Additives:These additives help keep the engine clean and prevent deposits. However, excessive detergents can lead to spark plug fouling.
- Anti-Wear Agents:These additives reduce friction and wear on moving parts, extending engine life.
Additional Resources
For further exploration and understanding of 2-cycle oil and mixing ratios, refer to the following reputable sources:
These resources provide valuable insights, practical guidance, and up-to-date information to enhance your knowledge and ensure safe and effective use of 2-cycle engines.
Articles and Videos
- “2-Cycle Oil: A Comprehensive Guide”– An in-depth article by Bob Vila that covers various aspects of 2-cycle oil, including its types, mixing ratios, and applications.
- “How to Mix 2-Cycle Oil with Gas”– A step-by-step video tutorial by Home Depot that demonstrates the proper technique for mixing 2-cycle oil with gasoline.
- “The Importance of 2-Cycle Oil”– A short video by Stihl that highlights the significance of using the correct 2-cycle oil for optimal engine performance.
Online Forums, How many ounces of 2 cycle oil per gallon
- “2-Cycle Engine Forum”– A dedicated online community where users can ask questions, share experiences, and discuss all things related to 2-cycle engines.
- “Small Engine Repair Forum”– A comprehensive forum that covers a wide range of small engine topics, including 2-cycle oil and mixing ratios.
Manufacturer Contact Information
- Stihl– 1-800-431-9003
- Husqvarna– 1-800-487-5962
- Echo– 1-800-673-2461
Final Thoughts
Now that you know how to mix 2 cycle oil with gasoline, you can keep your small engine running smoothly and efficiently. Just remember to always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific engine you’re using.
FAQ Resource: How Many Ounces Of 2 Cycle Oil Per Gallon
What is the standard ratio of 2 cycle oil to gasoline?
The standard ratio is 50:1, which means 50 parts gasoline to 1 part oil.
How do I convert ounces of 2 cycle oil to gallons?
There are 128 ounces in a gallon. So, to convert ounces to gallons, divide the number of ounces by 128.
What are the steps on how to mix 2 cycle oil with gasoline?
1. Measure out the correct amount of oil and gasoline. 2. Add the oil to the gasoline. 3.
Shake the container to mix the oil and gasoline together.
