How much 2 cycle oil in 1 gallon of gas – When it comes to operating 2-cycle engines, understanding how much 2-cycle oil to mix with 1 gallon of gas is crucial. The correct oil ratio ensures optimal engine performance, longevity, and emissions control. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the significance of oil-to-gas ratios, provide tips for accurate measurement, and discuss factors that influence the optimal ratio for different engine types and operating conditions.
Mixing 2-cycle oil with gasoline is not just about adding oil to the fuel tank. It requires precision and attention to detail to achieve the desired oil-to-gas ratio. This ratio varies depending on the engine type and the oil manufacturer’s recommendations.
Using too much oil can lead to engine fouling, increased emissions, and reduced performance, while too little oil can result in premature engine wear and damage.
2-Cycle Engine Oil Ratio
Using the correct oil ratio in 2-cycle engines is crucial for their proper functioning and longevity. The oil-to-gas ratio is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1 or 100:1, indicating the number of parts of gasoline to one part of oil.
The correct oil ratio ensures that the engine receives adequate lubrication to minimize friction and wear on moving parts, while preventing excessive oil buildup that can lead to fouling of spark plugs and exhaust ports.
Consequences of Incorrect Oil Ratio
- Too Much Oil:Using too much oil can result in excessive smoking, fouling of spark plugs and exhaust ports, and decreased engine performance due to reduced compression.
- Too Little Oil:Insufficient oil can lead to inadequate lubrication, increased friction and wear, potential engine damage, and premature failure.
Measuring 2-Cycle Oil: How Much 2 Cycle Oil In 1 Gallon Of Gas
Accurately measuring 2-cycle oil is crucial for ensuring the proper lubrication and performance of your engine. Various methods can be employed to achieve precise measurement, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Using Measuring Cups
Measuring cups are a simple and convenient tool for measuring 2-cycle oil. They come in various sizes, allowing you to choose the appropriate one for the required amount. To use a measuring cup, simply pour the oil into the cup up to the desired measurement line.
Ensure the oil level is level, not exceeding or falling short of the line.
Using Syringes
Syringes offer a more precise method of measuring 2-cycle oil, especially for smaller volumes. They are available in various sizes, including those specifically designed for measuring oil. To use a syringe, draw the plunger back to the desired measurement and insert the tip into the oil.
Slowly release the plunger, allowing the oil to fill the syringe up to the measurement line.
Other Measuring Tools
In addition to measuring cups and syringes, other tools can be used to measure 2-cycle oil, such as graduated cylinders or pipettes. Graduated cylinders provide accurate measurements for larger volumes, while pipettes are ideal for measuring small amounts with high precision.
Mixing 2-Cycle Oil with Gas
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your 2-cycle engine, it’s crucial to mix the 2-cycle oil with gasoline properly. This process involves combining the two liquids in the correct ratio, following the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Proper Mixing Technique
Mixing 2-cycle oil with gasoline is a simple but important task that requires careful attention to detail. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure proper mixing:
- Measure the gasoline and oil accurately:Determine the required amount of gasoline and 2-cycle oil based on the manufacturer’s recommended ratio.
- Add half of the gasoline to the fuel container:Pour approximately half of the measured gasoline into a clean, approved fuel container.
- Add the 2-cycle oil:Carefully measure and pour the required amount of 2-cycle oil into the fuel container.
- Mix thoroughly:Shake the fuel container vigorously for several minutes to ensure the oil and gasoline are thoroughly mixed.
- Add the remaining gasoline:Pour the remaining half of the gasoline into the fuel container and shake again to ensure even distribution.
Importance of Thorough Mixing
Thorough mixing is essential to ensure that the oil is evenly distributed throughout the gasoline. This helps prevent engine damage caused by insufficient lubrication or excessive oil buildup. When the oil is not properly mixed, it can lead to:
- Poor lubrication:Insufficient oil in the fuel mixture can result in inadequate lubrication of engine components, leading to increased friction, wear, and potential engine damage.
- Oil buildup:Excessive oil in the fuel mixture can cause oil buildup in the engine, resulting in reduced performance, spark plug fouling, and increased emissions.
Therefore, it’s crucial to take the time to mix the 2-cycle oil with gasoline thoroughly to ensure optimal engine performance and longevity.
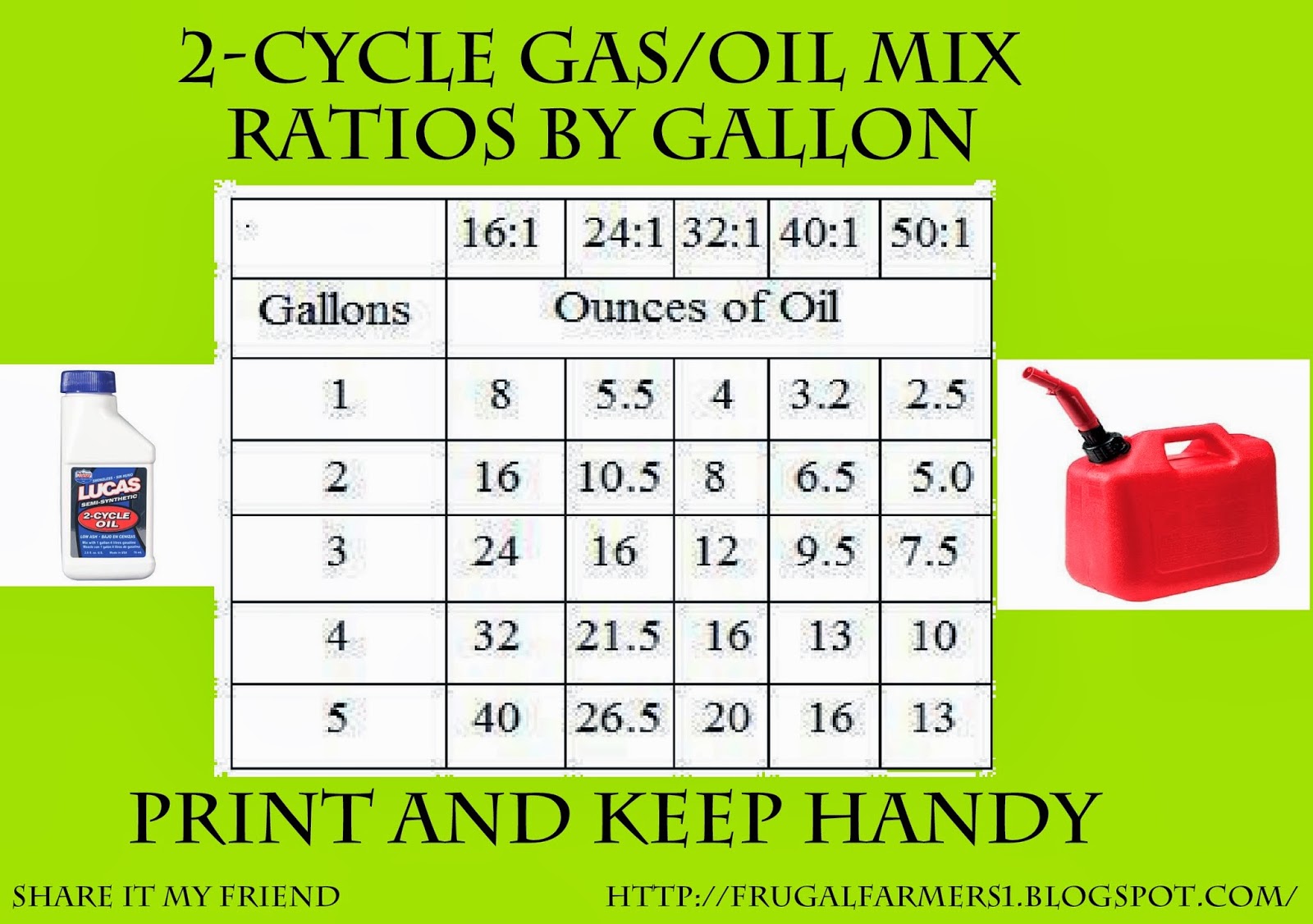
Oil-to-Gas Ratios
Different types of 2-cycle engines require specific oil-to-gas ratios to operate efficiently and prevent damage. It’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s recommended ratios to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the engine.
Common Oil-to-Gas Ratios
- General 2-cycle engines:25:1 to 50:1
- High-performance 2-cycle engines:32:1 to 40:1
- Small 2-cycle engines (e.g., chainsaws, trimmers):20:1 to 25:1
Note:Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the specific ratio recommended for your engine.
Factors Affecting Oil Ratio
The optimal oil-to-gas ratio for a 2-cycle engine can vary depending on several factors, including:
Engine Type
The type of 2-cycle engine, such as a chainsaw, outboard motor, or snowmobile, can affect the recommended oil ratio. Different engine designs and operating conditions may require specific oil ratios to ensure proper lubrication and performance.
Operating Conditions
The operating conditions of the engine, such as load, speed, and temperature, can also influence the oil ratio. Engines operating under heavy loads or high temperatures may require a higher oil ratio to provide adequate lubrication and prevent engine damage.
Oil Type
The type of 2-cycle oil used can also affect the recommended oil ratio. Different oil formulations may have varying viscosities and additive packages that can impact the lubrication properties and oil consumption. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific oil being used.
Consequences of Incorrect Oil Ratio

Incorrect oil-to-gas ratios can have significant consequences for 2-cycle engines. Using too little oil can lead to insufficient lubrication, causing increased friction and wear on engine components. This can result in reduced engine performance, shortened lifespan, and increased emissions.
On the other hand, using too much oil can cause excessive smoking, fouling of spark plugs, and reduced engine power. It can also lead to the formation of carbon deposits on the piston and exhaust system, further affecting engine performance and longevity.
If you’re concerned about your tires being stolen, there are a few things you can do to protect them. Here are some tips to help keep your tires safe. And if you’re ever wondering how long 1200 seconds is in minutes, check out this handy converter.
Engine Damage, How much 2 cycle oil in 1 gallon of gas
Insufficient lubrication due to an incorrect oil-to-gas ratio can cause excessive wear on moving parts, leading to premature engine failure.
Reduced Performance
Insufficient oil can lead to increased friction, reducing engine power and efficiency. Excessive oil, on the other hand, can cause spark plug fouling and carbon buildup, also affecting engine performance.
Increased Emissions
Incorrect oil-to-gas ratios can contribute to increased emissions, as unburned oil and fuel can escape through the exhaust system.
Car maintenance can be a hassle, but there are simple ways to prevent common issues like tire theft. Tips to prevent tire theft include using wheel locks and parking in well-lit areas. Additionally, knowing how long 1200 seconds is in minutes can be helpful for planning trips or other activities.
For example, 1200 seconds is equivalent to 20 minutes , which is a useful conversion to keep in mind.
Fouled Spark Plugs
Excessive oil can foul spark plugs, preventing them from igniting the air-fuel mixture properly, leading to engine misfiring and reduced performance.
Safety Precautions

Handling and mixing 2-cycle oil requires caution to ensure safety and prevent any adverse effects on health or the environment.
Always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, eye protection, and a mask, to avoid direct contact with the oil and minimize exposure to fumes.
Proper Handling and Storage
- Store 2-cycle oil in a well-ventilated area, away from heat sources and direct sunlight.
- Keep containers tightly sealed to prevent spills and contamination.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes, as the oil can cause irritation or allergic reactions.
- In case of accidental contact, rinse the affected area thoroughly with water and seek medical attention if necessary.
- Dispose of used oil and empty containers responsibly, in accordance with local regulations.
Concluding Remarks
Mixing 2-cycle oil with gasoline is a crucial aspect of maintaining the health and performance of 2-cycle engines. By understanding the significance of oil-to-gas ratios, accurately measuring the oil, and considering factors that influence the optimal ratio, you can ensure that your engine operates at its best.
Remember to always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and follow safety precautions when handling and mixing 2-cycle oil.
FAQ
What happens if I use too much 2-cycle oil?
Using too much 2-cycle oil can lead to engine fouling, increased emissions, and reduced performance. It can also cause spark plug fouling and excessive smoke.
What happens if I use too little 2-cycle oil?
Using too little 2-cycle oil can result in premature engine wear and damage. It can also lead to increased friction and heat, which can cause engine seizure.
How do I accurately measure 2-cycle oil?
You can use a measuring cup, syringe, or other tools specifically designed for measuring 2-cycle oil. Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the correct oil-to-gas ratio.
