Delve into the intricate world of nitrogen cycling with our comprehensive Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet with Answers. This resource offers a detailed exploration of the nitrogen cycle’s significance, processes, and human impact, providing a solid foundation for understanding this crucial biogeochemical process.
Throughout this guide, we will embark on a journey through the nitrogen cycle’s stages, from nitrogen fixation to denitrification. Along the way, we will uncover the vital role of bacteria in each step and delve into the consequences of human activities on this delicate cycle.
Nitrogen Fixation

Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen gas (N2) in the atmosphere is converted into ammonia (NH3) or other nitrogen-containing compounds. This process is essential for life on Earth because nitrogen is a key component of proteins, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules.
Nitrogen fixation is carried out by a variety of bacteria and archaea. These microorganisms have the ability to convert N2 into NH3 using an enzyme called nitrogenase. Nitrogenase is a complex enzyme that requires a lot of energy to function.
As a result, nitrogen fixation is a relatively slow process.
Do not overlook the opportunity to discover more about the subject of electric bike rentals.
Role of Bacteria in Nitrogen Fixation, Nitrogen cycle worksheet with answers
Bacteria play a critical role in the nitrogen cycle. They are the only organisms that can fix nitrogen gas from the atmosphere. There are two main types of nitrogen-fixing bacteria: symbiotic and free-living.
Symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in close association with plants. They form nodules on the roots of plants, where they fix nitrogen gas and convert it into ammonia. The ammonia is then used by the plant to produce proteins and other nitrogen-containing compounds.
Free-living nitrogen-fixing bacteria live independently of plants. They fix nitrogen gas and convert it into ammonia, which is then released into the soil. The ammonia can then be used by plants or other microorganisms.
Nitrification
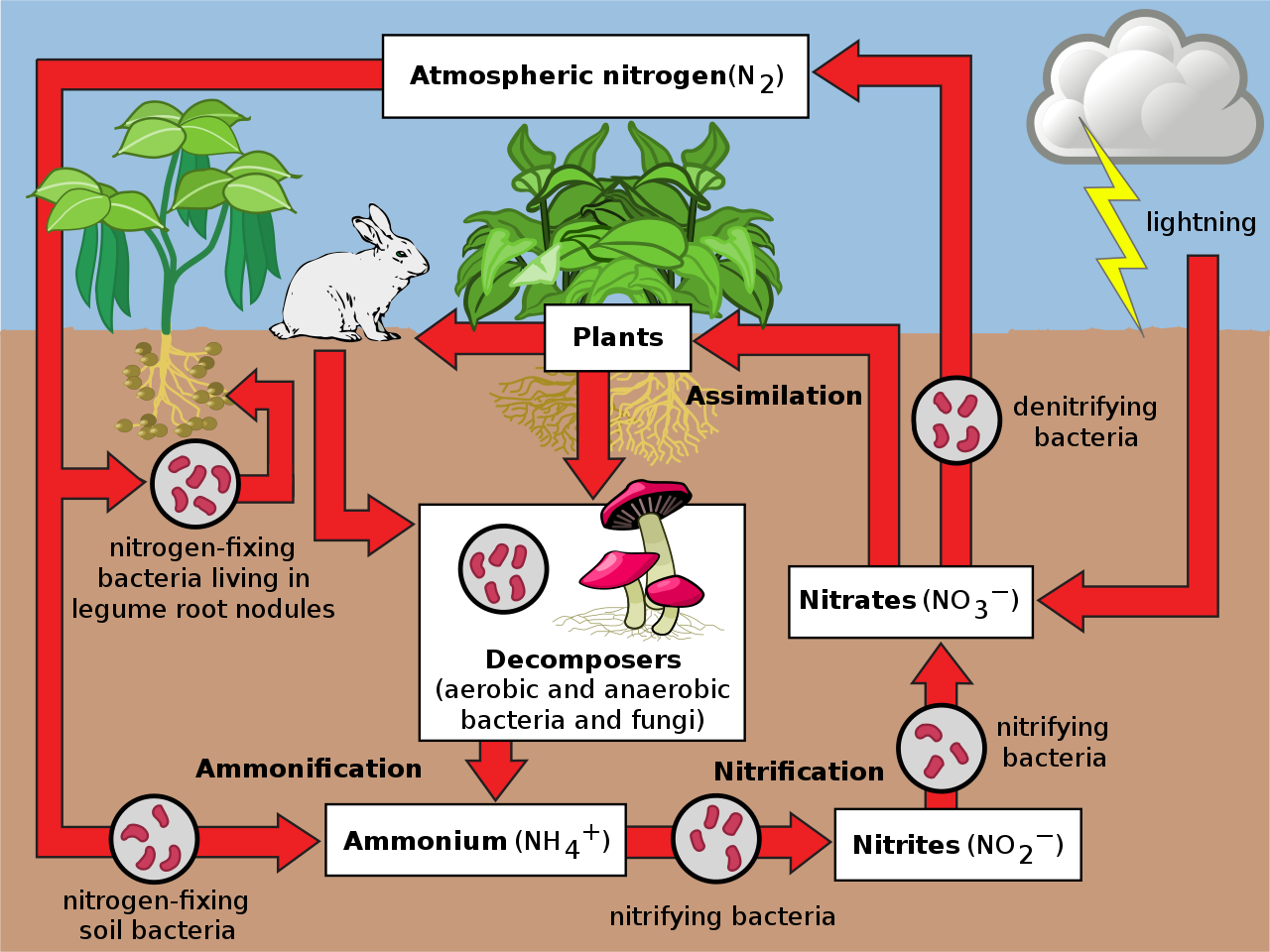
Nitrification is the process of converting ammonia into nitrate. It is carried out by two groups of bacteria: Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
Nitrosomonas bacteria oxidize ammonia to nitrite. This reaction is represented by the following equation:
Nitrobacter bacteria then oxidize nitrite to nitrate. This reaction is represented by the following equation:
Obtain direct knowledge about the efficiency of electric bike rentals lake tahoe through case studies.
Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle because it converts ammonia, which is toxic to plants, into nitrate, which is a nutrient that plants can use for growth.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet with Answers serves as an invaluable tool for comprehending the intricate workings of the nitrogen cycle. By delving into its processes and implications, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance of our ecosystems and the need for responsible stewardship of our planet’s resources.
FAQ Explained: Nitrogen Cycle Worksheet With Answers
What is the nitrogen cycle?
The nitrogen cycle is a biogeochemical process that transforms nitrogen into various forms, ensuring its availability for living organisms.
What is the role of bacteria in the nitrogen cycle?
Bacteria play crucial roles in nitrogen fixation, nitrification, ammonification, and denitrification, enabling the conversion of nitrogen between different forms.
How do human activities impact the nitrogen cycle?
Human activities, such as fertilizer use and fossil fuel combustion, can disrupt the nitrogen cycle, leading to environmental issues like eutrophication and climate change.
