Embark on a fascinating journey through the printable life cycle of a chicken, an essential guide that unveils the intricate stages of this remarkable creature’s existence. From the humble beginnings of an egg to the bustling activity of a laying hen, this narrative explores the captivating world of poultry farming.
Unravel the secrets of chicken development, from the delicate formation of an egg to the remarkable transformation into a fully grown bird. Discover the intricacies of each stage, the challenges faced, and the practices employed to ensure the well-being of these feathered friends.
Introduction
Understanding the life cycle of a chicken is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps farmers and poultry enthusiasts optimize their breeding and production practices, ensuring the well-being and productivity of their flocks. Secondly, it provides insights into the developmental stages and unique characteristics of chickens at different points in their lives.
This knowledge is valuable for both scientific research and educational purposes.
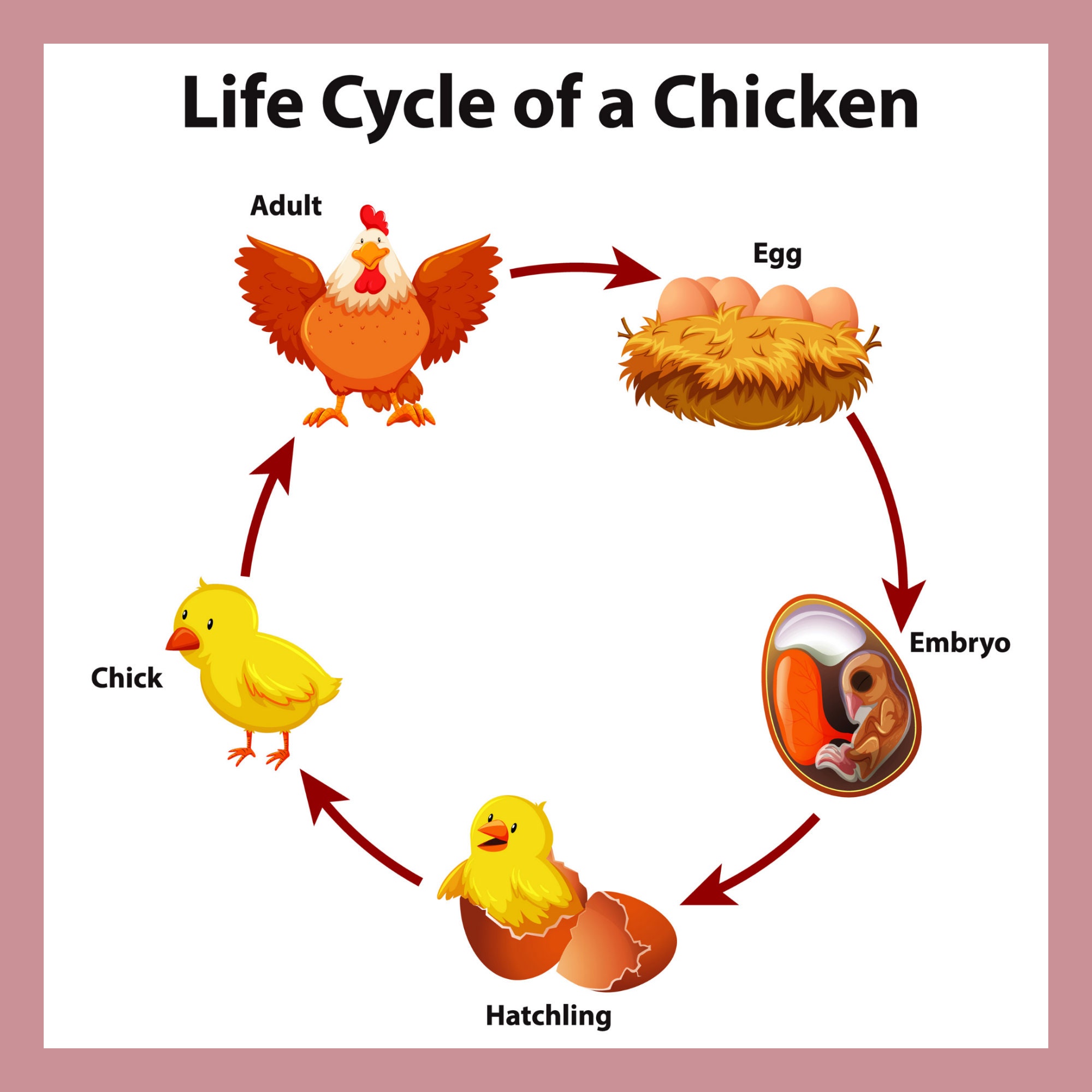
The life cycle of a chicken involves distinct stages, each characterized by specific physical, behavioral, and physiological changes. These stages include the embryonic stage, the chick stage, the pullet stage, the hen stage, and the rooster stage.
, Printable life cycle of a chicken
[detailed content here]
Investigate the pros of accepting rent a trike near me in your business strategies.
Pullet
As growers reach sexual maturity, they transition into pullets. This transition is marked by significant physiological changes, including the development of the reproductive system and the onset of egg production.
Nutrition and Housing
Proper nutrition and housing are crucial for pullets’ health and productivity. Their diet should be rich in protein, calcium, and other nutrients essential for egg production. Pullets also require adequate space, ventilation, and lighting to ensure their well-being and egg-laying capabilities.
Laying Hen
The laying hen stage is a crucial phase in the chicken’s life cycle, where the hens reach sexual maturity and begin laying eggs. This stage requires specific care and management practices to ensure optimal egg production and hen well-being.
The egg-laying process involves the development and release of an egg from the hen’s reproductive system. It begins with the formation of the yolk in the ovary, which is then enclosed by the albumen (egg white) and the shell. The egg is then laid through the cloaca, the common opening for the digestive, urinary, and reproductive systems.
Factors Affecting Egg Production
Several factors influence egg production in laying hens:
- Nutrition:A balanced diet containing essential nutrients, including protein, calcium, and vitamins, is vital for optimal egg production.
- Lighting:Hens are sensitive to light, and the duration and intensity of light exposure can affect their egg-laying behavior.
- Management Practices:Proper housing, ventilation, and hygiene practices contribute to the health and well-being of laying hens, which in turn impacts egg production.
Common Challenges Faced by Laying Hens
Laying hens may encounter various challenges that can affect their egg production and health:
- Nutritional Deficiencies:Inadequate or unbalanced diets can lead to reduced egg production, poor egg quality, and health issues.
- Diseases and Infections:Diseases such as Marek’s disease, Newcastle disease, and infectious bronchitis can significantly impact egg production and hen mortality.
- Environmental Stress:Extreme temperatures, overcrowding, and poor ventilation can cause stress and reduce egg production.
- Pecking and Cannibalism:In overcrowded or stressful conditions, hens may engage in pecking and cannibalism, which can lead to injuries and reduced egg production.
Broiler
Broilers are chickens specifically bred for meat production, distinct from layer chickens raised for egg production. Broiler chickens are characterized by rapid growth and a high feed conversion ratio, resulting in a large amount of meat in a short period.
Broiler management practices and nutritional requirements differ from those of layer chickens. Broilers are typically raised in large, controlled environments with strict temperature and lighting regimens to optimize growth. Their diet is formulated to support rapid muscle development and includes high levels of protein and energy.
Factors Influencing Broiler Growth and Meat Quality
Several factors influence broiler growth and meat quality, including:
- Genetics:The breed of broiler and its genetic makeup significantly impact growth rate, feed conversion efficiency, and meat quality.
- Nutrition:A balanced diet providing adequate protein, energy, vitamins, and minerals is essential for optimal growth and meat quality.
- Management Practices:Proper housing, temperature control, ventilation, and hygiene practices are crucial for broiler health and performance.
- Health:Diseases and parasites can adversely affect broiler growth and meat quality, necessitating proper vaccination and biosecurity measures.
- Environment:Temperature, humidity, and air quality within the broiler house play a significant role in growth and meat quality.
Spent Hen: Printable Life Cycle Of A Chicken

Spent hens are female chickens that have reached the end of their productive laying cycle. This typically occurs around 18 to 24 months of age, when their egg production declines significantly.
The end of the laying cycle is a natural process in the life of a hen. As they age, their reproductive organs begin to decline, and their bodies start to allocate more energy to other functions, such as molting and feather growth.
Options for Spent Hens
There are several options available for spent hens:
- Molting:Spent hens can be induced to molt, which is a natural process where they lose their old feathers and grow new ones. Molting can help to improve their health and egg production, and it can extend their laying cycle for a few more months.
- Rehoming:Spent hens can also be rehomed to backyard flocks or sanctuaries, where they can live out the rest of their lives in a more natural environment.
- Processing:Spent hens can also be processed for meat. This is typically the least desirable option, as spent hens are not as tender or flavorful as younger chickens.
Ethical Considerations
There are several ethical considerations related to spent hen management:
- Welfare:Spent hens should be treated humanely, regardless of their productive value. They should have access to adequate food, water, shelter, and veterinary care.
- Environmental impact:The processing of spent hens can have a negative impact on the environment. Spent hens can also be a source of pollution if they are not properly disposed of.
- Consumer responsibility:Consumers should be aware of the ethical implications of purchasing eggs and chicken meat. They should choose products that come from farms that treat their hens humanely.
Processing
Processing refers to the steps involved in slaughtering and preparing chickens for human consumption. It is a critical stage in the poultry industry that requires strict adherence to food safety and hygiene standards.
The process typically begins with live chickens being transported to a processing plant, where they undergo a series of inspections and preparations. These include stunning, bleeding, scalding, defeathering, evisceration, chilling, and packaging.
Stunning
Stunning is a humane method of rendering chickens unconscious before slaughter. This is typically achieved through electrical or mechanical means to minimize pain and distress to the animals.
Bleeding
After stunning, the chickens are bled by severing major blood vessels in the neck. This step is crucial for ensuring proper blood removal and preventing contamination of the meat.
Scalding
Scalding involves immersing the chickens in hot water to loosen their feathers. This facilitates the removal of feathers during the subsequent defeathering process.
Defeathering
Defeathering is the process of removing feathers from the chicken carcasses. This can be done manually or mechanically using specialized equipment.
Evisceration
Evisceration involves removing the internal organs, including the digestive tract, lungs, heart, and liver. This step is performed by skilled workers who ensure that the organs are removed cleanly and without damaging the meat.
Chilling
After evisceration, the chicken carcasses are chilled rapidly to prevent bacterial growth and preserve their quality. This is typically achieved by immersing the carcasses in cold water or using air-cooling systems.
Packaging
Once chilled, the chicken carcasses are packaged and labeled according to their intended use. Packaging options include whole chickens, cut-up parts, and ground chicken.
Food Safety and Hygiene
Maintaining food safety and hygiene throughout the processing operation is paramount. This involves implementing strict sanitation protocols, adhering to temperature control guidelines, and ensuring that all equipment and surfaces are thoroughly cleaned and disinfected.
Marketing
Marketing plays a crucial role in promoting and selling chicken products, connecting producers with consumers and influencing consumer choices. Various channels and strategies are employed to reach target audiences and drive demand.
Factors influencing consumer demand and preferences for chicken products include health consciousness, convenience, taste, price, and sustainability. Emerging trends and innovations in chicken marketing include digital marketing, personalized marketing, and value-added products.
Examine how cycle works sanitation bill pay can boost performance in your area.
Channels and Strategies
- Retail Stores:Supermarkets, grocery stores, and butcher shops are primary channels for selling fresh and processed chicken products directly to consumers.
- Food Service:Restaurants, fast-food chains, and institutional kitchens purchase chicken products in bulk for use in their menu offerings.
- Online Marketplaces:E-commerce platforms and meal-kit delivery services provide convenient options for consumers to purchase chicken products online.
- Direct-to-Consumer:Some producers sell chicken products directly to consumers through their own websites or farmers’ markets.
- Export Markets:International trade is a significant channel for marketing chicken products to other countries.
Factors Influencing Consumer Demand and Preferences
- Health Consciousness:Consumers increasingly seek healthier food options, driving demand for low-fat, high-protein chicken products.
- Convenience:Ready-to-cook or pre-cooked chicken products appeal to consumers seeking quick and convenient meal solutions.
- Taste:Flavor and texture are key factors influencing consumer preferences for chicken products.
- Price:Affordability is a significant consideration for many consumers, particularly for bulk purchases.
- Sustainability:Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, preferring chicken products from farms that prioritize animal welfare and reduce their environmental footprint.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
- Digital Marketing:Social media, email campaigns, and online advertising are used to reach and engage target audiences.
- Personalized Marketing:Data analytics and targeted marketing strategies allow companies to tailor marketing messages to specific consumer preferences.
- Value-Added Products:Chicken products with added flavors, marinades, or ready-to-cook sauces provide convenience and enhance consumer experience.
Final Thoughts
As we conclude our exploration of the printable life cycle of a chicken, a profound appreciation for the complexities and wonders of poultry farming emerges. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, from the initial spark of life within an egg to the culmination of the laying cycle.
Understanding these stages empowers us to make informed choices, ensuring the ethical treatment and sustainable practices that define modern poultry farming.
FAQ Overview
What are the key stages in a chicken’s life cycle?
The key stages in a chicken’s life cycle include the egg, chick, grower, pullet, laying hen, broiler, spent hen, processing, and marketing.
What factors influence egg quality and hatchability?
Egg quality and hatchability are influenced by factors such as the age and health of the hen, nutrition, environmental conditions, and storage practices.
What are the common challenges faced by chicks during the grower stage?
Common challenges faced by chicks during the grower stage include diseases, nutritional deficiencies, and environmental stressors such as temperature fluctuations and overcrowding.
