Carbon cycle questions and answers pdf – Welcome to the fascinating realm of the carbon cycle, where the intricate dance of carbon through our planet’s ecosystems unfolds. This comprehensive guide, presented in a PDF format, delves into the fundamental processes, natural sinks, and anthropogenic sources that shape the carbon cycle.
Get ready to unravel the secrets of carbon’s journey and its profound impact on our climate.
As we navigate through this guide, you’ll discover the role of forests, oceans, and wetlands as nature’s carbon guardians. We’ll also explore the human-induced sources of carbon emissions and their contribution to climate change. The potential solutions, such as carbon capture and storage, will be examined, along with international agreements and mitigation strategies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Anthropogenic Carbon Sources
Human activities significantly contribute to the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and global warming. These human-induced carbon emissions primarily stem from the combustion of fossil fuels for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes.
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global carbon dioxide emissions from human activities reached approximately 36.3 billion metric tons in 2019. The energy sector, including electricity generation and transportation, accounted for the majority of these emissions, contributing around 73%.
Industrial processes, such as cement production and steel manufacturing, were responsible for an estimated 23% of global carbon dioxide emissions.
Transportation Sector
The transportation sector is a major contributor to carbon emissions, primarily due to the reliance on fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Road transportation, including cars, trucks, and buses, accounts for the largest share of emissions within this sector. Air travel and shipping also contribute significantly to transportation-related carbon emissions.
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes, such as cement production, steel manufacturing, and chemical production, release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Cement production, in particular, is a highly carbon-intensive process, as it involves the calcination of limestone, which releases large quantities of carbon dioxide.
Electricity Generation
Electricity generation is another significant source of carbon emissions, primarily due to the widespread use of fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, in power plants. The combustion of these fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas concentrations.
Impact on Climate Change
The increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide contributes to climate change through its role as a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to an increase in global temperatures. The warming effect of carbon dioxide is a major contributor to the observed increase in global average temperatures since the late 19th century.
Effects on Global Temperatures and Weather Patterns
Elevated levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enhance the greenhouse effect, resulting in higher global temperatures. This warming can lead to changes in weather patterns, such as increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, including heat waves, droughts, floods, and storms.
Do not overlook explore the latest data about best flat pedals for gravel bike.
Changes in precipitation patterns and sea level rise are also associated with the warming climate due to increased carbon dioxide levels.
Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a process of capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial and power plant sources, transporting it, and storing it underground in geological formations. This technology has the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Technologies for Carbon Capture, Carbon cycle questions and answers pdf
There are several technologies used for carbon capture:
Pre-combustion capture
In this process, the fuel is converted into a gas, and the CO2 is removed before combustion.
Post-combustion capture
This process captures CO2 from the flue gas after combustion.
Oxyfuel combustion
This process burns fuel in pure oxygen, producing a flue gas that is mostly CO2.
Benefits and Challenges of CCS
Benefits of CCS:
Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
CCS can significantly reduce CO2 emissions from industrial and power plant sources.
Clean energy production
CCS can enable the continued use of fossil fuels while reducing their environmental impact.
Job creation
CCS projects can create new jobs in the energy sector. Challenges of CCS:
High cost
CCS technologies are currently expensive to implement.
Transportation and storage
Transporting and storing large amounts of CO2 can be logistically challenging and costly.
Public perception
There are concerns about the safety and environmental impacts of CCS.
Policy and Mitigation Strategies
International agreements and policies have been established to tackle the issue of carbon emissions and their impact on climate change. The Kyoto Protocol, adopted in 1997, set binding targets for developed countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, aims to limit global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, with efforts to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
These agreements provide a framework for countries to collaborate and implement mitigation strategies to reduce carbon emissions.
Examples of Successful Mitigation Strategies
Various countries have implemented successful mitigation strategies to reduce carbon emissions. These include:
- Carbon pricing:Countries like the United Kingdom and Canada have implemented carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, to incentivize businesses and individuals to reduce emissions.
- Renewable energy policies:Many countries have adopted policies to promote the development and use of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy efficiency measures:Governments have implemented energy efficiency standards for buildings, appliances, and vehicles to reduce energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
- Forest conservation and afforestation:Countries have recognized the role of forests in carbon sequestration and have implemented policies to protect existing forests and promote afforestation efforts.
Carbon Offsets and Trading

Carbon offsets and trading are mechanisms designed to reduce global carbon emissions by creating financial incentives for individuals, organizations, and governments to reduce their carbon footprint.
Carbon offsets represent a specific amount of carbon dioxide or its equivalent that has been removed from the atmosphere or prevented from being emitted. These offsets can be generated through various activities, such as planting trees, investing in renewable energy projects, or adopting energy-efficient practices.
Role of Carbon Offsets and Trading in Reducing Emissions
Carbon trading involves the buying and selling of carbon credits, which represent the ownership of carbon offsets. Entities that have excess carbon offsets can sell them to those that need to reduce their emissions to meet regulatory requirements or voluntary commitments.
By creating a market for carbon offsets, these mechanisms encourage investment in emission-reduction projects and technologies. They also provide flexibility for entities to meet their emission targets in a cost-effective manner.
Additionally, carbon offsets and trading can support sustainable development and environmental conservation by promoting investments in projects that benefit both the climate and local communities.
You also will receive the benefits of visiting best flat bar gravel bikes today.
Research and Innovation
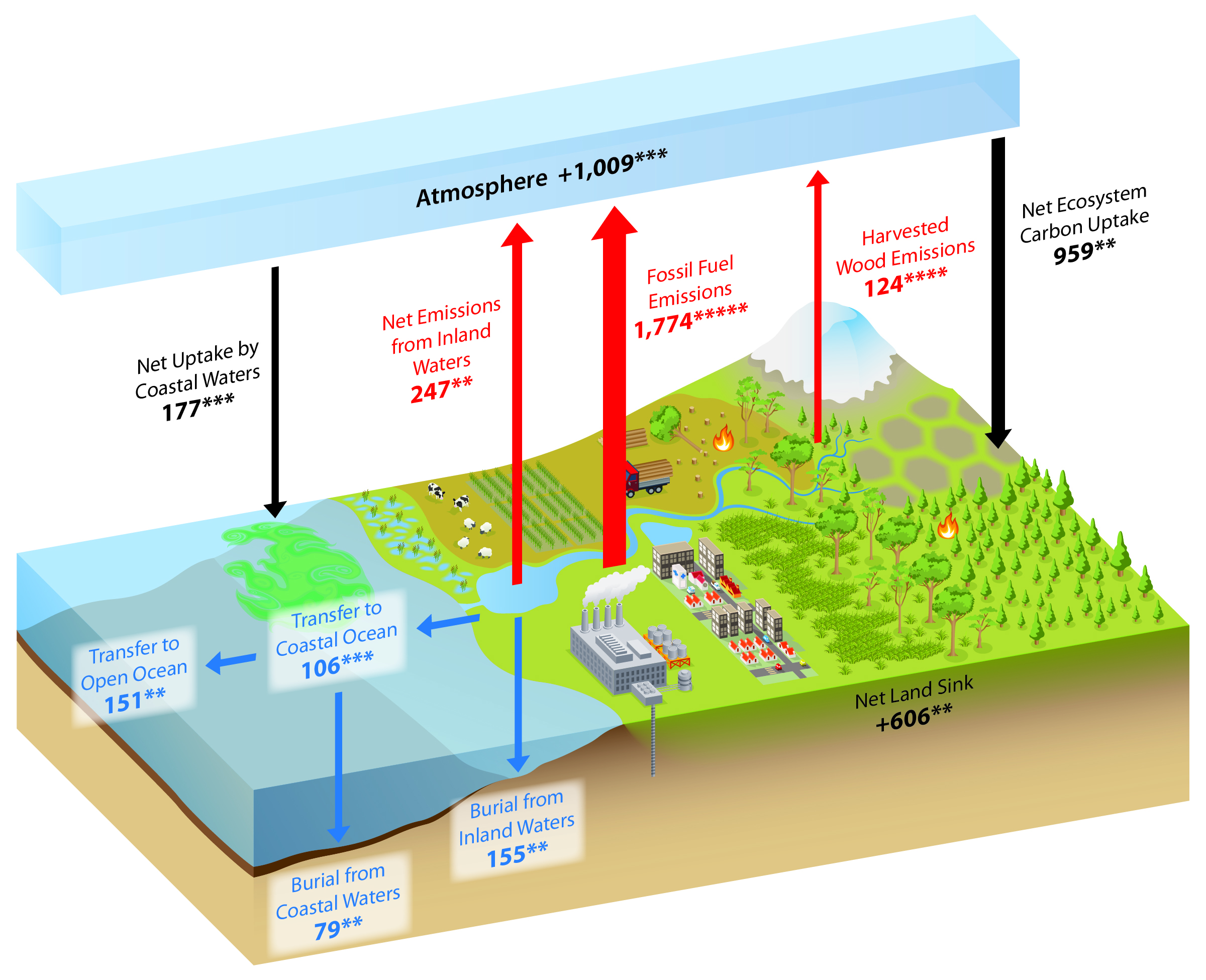
Ongoing research and innovations in carbon cycle science are crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate climate change. These efforts encompass a wide range of disciplines, including atmospheric chemistry, oceanography, ecology, and engineering.
One key area of research focuses on improving our understanding of the carbon cycle’s natural processes. This involves studying the interactions between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and biosphere to identify potential vulnerabilities and areas where human activities may have a significant impact.
Emerging Technologies for Carbon Capture, Storage, and Utilization
Research and innovation are also driving the development of emerging technologies for carbon capture, storage, and utilization. These technologies have the potential to play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): CCS involves capturing carbon dioxide (CO2) from industrial sources or the atmosphere and storing it underground in geological formations or the ocean. This technology has the potential to significantly reduce emissions from power plants, factories, and other industrial processes.
- Carbon Utilization: Carbon utilization technologies convert CO2 into valuable products, such as fuels, chemicals, and building materials. This approach not only reduces emissions but also creates economic opportunities.
Outcome Summary: Carbon Cycle Questions And Answers Pdf
In conclusion, the carbon cycle is a dynamic and complex system that plays a crucial role in regulating our planet’s climate. Understanding the processes and interactions within the carbon cycle is essential for addressing the challenges of climate change. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the carbon cycle, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and contribute to a sustainable future.
User Queries
What is the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle is the continuous movement of carbon between the atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle?
Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agriculture, release large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting the natural balance of the carbon cycle.
What are the consequences of increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels?
Increased atmospheric carbon dioxide levels contribute to climate change, leading to rising global temperatures, more extreme weather events, and sea level rise.
What are some solutions to mitigate climate change?
Solutions to mitigate climate change include reducing carbon emissions through renewable energy, energy efficiency, and carbon capture and storage.
