How long should a freezer run between cycles – Understanding how long a freezer should run between cycles is crucial for maintaining optimal food preservation and energy efficiency. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of freezer operation, exploring factors that influence cycle duration and providing troubleshooting tips for addressing common issues.
Freezer Operation Basics: How Long Should A Freezer Run Between Cycles

A freezer is a vital kitchen appliance that helps preserve food for longer durations by maintaining extremely low temperatures. Understanding the basics of freezer operation can help you maintain your freezer efficiently and ensure optimal food preservation.
If you’re considering upgrading your tires, you might be wondering how long Pirelli P Zero tires last. These tires are known for their performance and durability, but their lifespan can vary depending on factors like driving habits and road conditions.
On average, you can expect Pirelli P Zero tires to last between 25,000 and 40,000 miles.
Purpose of Compressor and Condenser
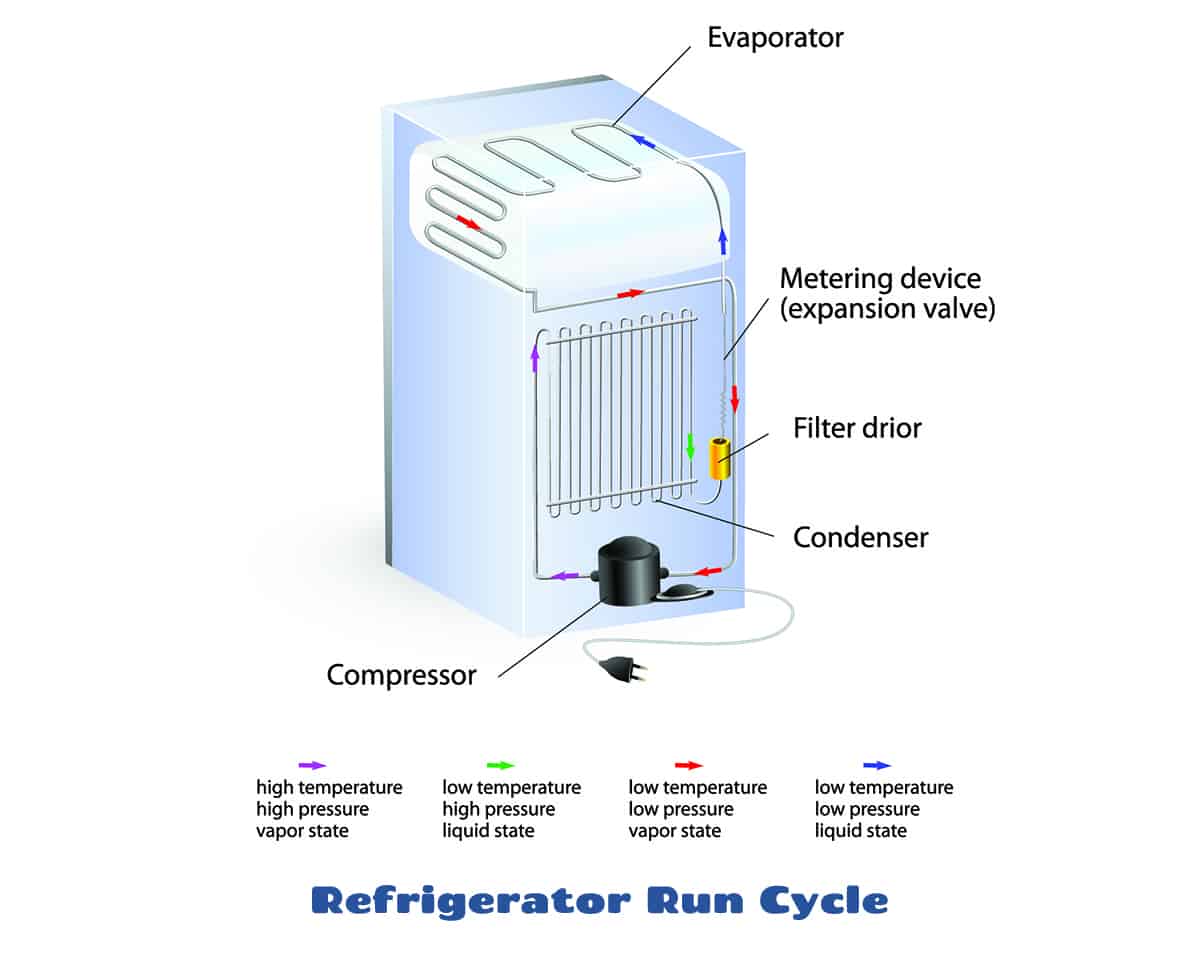
The freezer’s compressor is the heart of the cooling system. It compresses refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature. This high-pressure gas then flows into the condenser, which is usually located at the back or bottom of the freezer. In the condenser, the gas releases heat to the surrounding air, causing it to condense into a liquid.
Role of Thermostat
The thermostat is a crucial component that regulates the freezer’s temperature. It monitors the temperature inside the freezer and activates the compressor when the temperature rises above a certain set point. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat turns off the compressor, allowing the freezer to maintain a stable temperature.
Typical Freezer Cycle
The freezer cycle typically involves four main steps:
- Cooling:The compressor turns on and circulates refrigerant through the system, absorbing heat from the freezer’s interior.
- Condensation:The compressed refrigerant gas releases heat in the condenser, turning into a liquid.
- Expansion:The liquid refrigerant flows through an expansion valve, reducing its pressure and temperature.
- Evaporation:The low-pressure refrigerant flows through the evaporator coils inside the freezer, absorbing heat from the food and turning back into a gas.
This cycle repeats continuously, maintaining a constant low temperature inside the freezer.
Factors Affecting Freezer Cycle Duration
The duration of a freezer’s cycle is influenced by various factors that impact the rate at which it needs to cool down and maintain its internal temperature. Understanding these factors can help you optimize freezer performance and ensure the longevity of your food.
The lifespan of Pirelli P Zero tires depends on various factors, including driving habits, road conditions, and tire maintenance. For a general estimate, you can refer to how long do pirelli p zero tires last. Additionally, when converting 107 km to mph, it’s worth noting that 107 km is approximately 66.48 mph, which can be a useful conversion for drivers.
Ambient Temperature
The ambient temperature outside the freezer significantly affects its cycle length. When the surrounding temperature is high, the freezer must work harder to maintain its internal temperature, leading to longer cycles. Conversely, in cooler environments, the freezer has less work to do, resulting in shorter cycles.
Freezer Load
The amount of food stored in the freezer affects its cycle duration. A heavily loaded freezer requires more cooling to maintain its temperature, resulting in longer cycles. This is because the food itself absorbs heat and contributes to the freezer’s internal temperature rise.
If you’re planning a road trip, you may be wondering how fast is 107 km in mph. The answer is 66.5 mph. So, if you’re driving at 107 km/h, you’re traveling at a speed that’s equivalent to 66.5 miles per hour.
Freezer Door Openings
Frequent freezer door openings allow warm air to enter the freezer, raising its internal temperature. To compensate for this, the freezer must run longer cycles to bring the temperature back down to the desired level. Therefore, minimizing unnecessary freezer door openings is crucial for efficient operation.
Ideal Freezer Cycle Length

Determining the optimal freezer cycle length involves balancing several factors, including the ambient temperature, the freezer’s capacity and insulation, and the frequency of door openings.
Maintaining a consistent cycle length is crucial for ensuring the freezer’s efficient operation and the preservation of food. Excessively long cycles can lead to unnecessary energy consumption, while excessively short cycles may not provide adequate cooling, resulting in food spoilage.
Guidelines for Determining Optimal Cycle Length
- Ambient Temperature:Higher ambient temperatures require shorter cycle lengths to maintain a consistent internal temperature.
- Freezer Capacity and Insulation:Larger freezers with thicker insulation require longer cycle lengths to cool down and maintain temperature.
- Frequency of Door Openings:Frequent door openings allow warm air to enter the freezer, requiring shorter cycle lengths to compensate.
Benefits of Maintaining a Consistent Cycle Length, How long should a freezer run between cycles
- Energy Efficiency:Consistent cycle lengths prevent excessive energy consumption by avoiding unnecessary cooling.
- Food Preservation:Maintaining a consistent temperature ensures optimal food preservation and prevents spoilage.
- Reduced Maintenance:Avoiding excessively long or short cycles minimizes strain on the freezer’s compressor, extending its lifespan.
Consequences of Excessively Long or Short Freezer Cycles
Excessively Long Cycles
- Energy Waste:Unnecessary energy consumption increases utility bills and contributes to environmental impact.
- Defrosting Issues:Excessive cooling can lead to excessive frost buildup, requiring more frequent defrosting.
Excessively Short Cycles
- Food Spoilage:Inadequate cooling may not maintain a safe temperature, leading to food spoilage and potential health risks.
- Compressor Strain:Frequent short cycles put strain on the compressor, potentially reducing its lifespan.
Troubleshooting Freezer Cycle Issues
Identifying and addressing issues causing extended freezer cycles is crucial for maintaining optimal freezer operation and preventing potential food spoilage. Various factors can contribute to excessive cycle length, and understanding the underlying causes is essential for effective troubleshooting.
Common Causes of Extended Freezer Cycles
- Overcrowded Freezer: Excess food items can block airflow, impairing cooling efficiency and leading to extended cycles.
- Damaged or Faulty Door Seal: A compromised door seal allows warm air to enter the freezer, increasing the workload on the compressor and resulting in longer cycles.
- Defrost System Malfunction: A faulty defrost system can lead to ice buildup on the evaporator coils, reducing cooling capacity and causing the freezer to run continuously.
- Condenser Coils Blocked by Dust or Debris: Dirty condenser coils impede heat dissipation, reducing the freezer’s ability to cool effectively and resulting in extended cycles.
- Oversized Freezer for the Space: A freezer that is too large for the available space may struggle to maintain a consistent temperature, leading to frequent cycling.
Troubleshooting Steps for Addressing Excessive Cycle Length
To address excessive freezer cycle length, follow these troubleshooting steps:
- Check Freezer Load: Remove excess food items and ensure proper airflow within the freezer.
- Inspect Door Seal: Examine the door seal for any tears, gaps, or damage. Replace the seal if necessary.
- Test Defrost System: Manually initiate a defrost cycle and observe if the ice melts properly. If not, consider replacing the defrost timer or defrost heater.
- Clean Condenser Coils: Vacuum or brush away any dust or debris from the condenser coils to improve heat dissipation.
- Assess Freezer Size: Determine if the freezer is appropriately sized for the available space. If not, consider replacing it with a smaller or larger model.
Potential Solutions for Shortening Freezer Cycles When Necessary
In certain situations, it may be necessary to shorten freezer cycle length to optimize performance. Consider the following solutions:
- Use a Fan: Install a small fan inside the freezer to circulate air and improve cooling efficiency.
- Lower Freezer Temperature: Adjust the thermostat to a slightly lower temperature setting, allowing the freezer to maintain a cooler temperature with shorter cycles.
- Add Thermal Mass: Place a frozen water bottle or ice packs inside the freezer to act as a thermal mass, absorbing heat and reducing the compressor’s workload.
Final Review
By adhering to the guidelines Artikeld in this guide, you can ensure that your freezer operates efficiently, preserving the quality of your frozen foods while minimizing energy consumption. Remember, regular maintenance and monitoring are key to extending the lifespan of your freezer and ensuring its optimal performance.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the ideal freezer temperature?
The optimal freezer temperature is 0°F (-18°C) or below.
How often should I defrost my freezer?
Defrost your freezer every 6-12 months, or more frequently if it accumulates excessive frost.
Why is my freezer running constantly?
Constant freezer operation could indicate a faulty thermostat, a clogged condenser, or a damaged door seal.
Can I shorten the freezer cycle length?
Yes, you can shorten the cycle length by reducing the amount of food in the freezer, minimizing door openings, and ensuring proper ventilation around the appliance.
