How long to let fish tank cycle before adding fish – The topic of how long to cycle a fish tank before adding fish is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of your aquatic pets. Before introducing new fish to your tank, it’s essential to allow the tank to go through a cycling process that establishes a stable biological ecosystem.
This article delves into the details of tank cycling, its benefits, and provides a timeline for completing the process successfully.
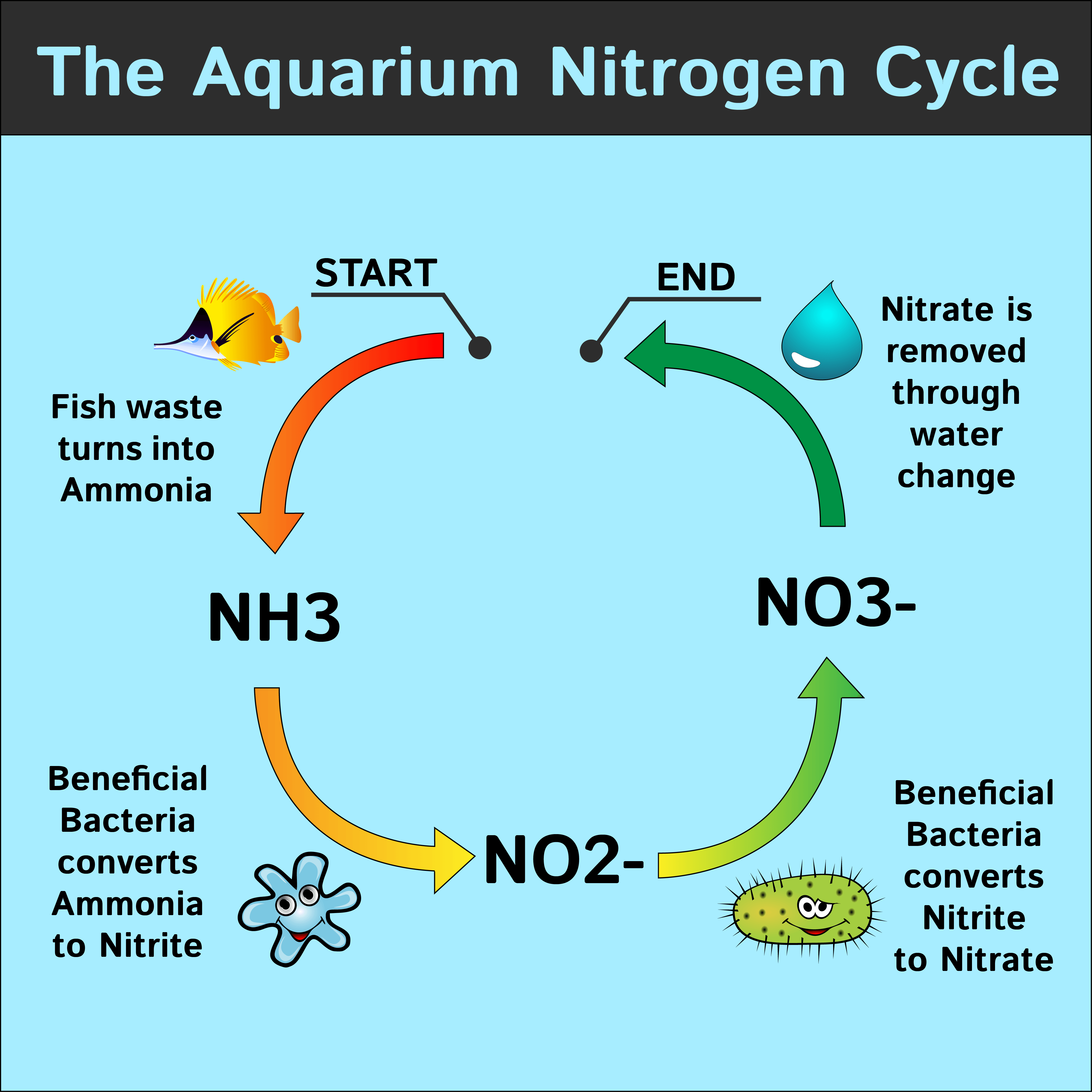
Cycling a fish tank involves establishing a colony of beneficial bacteria that convert toxic ammonia and nitrite into less harmful nitrate. This process takes time, typically several weeks, and requires careful monitoring of water parameters to ensure the safety of any fish introduced to the tank.
Nitrogen Cycle and Tank Cycling
The nitrogen cycle is a natural process that occurs in all aquariums. It is the process by which harmful nitrogen compounds are converted into less harmful forms. The nitrogen cycle is essential for maintaining a healthy aquarium, as it prevents the buildup of toxic nitrogen compounds that can harm fish and other aquatic life.Tank cycling is the process of establishing the nitrogen cycle in a new aquarium.
This process typically takes several weeks to complete. During this time, the beneficial bacteria that are responsible for the nitrogen cycle will colonize the aquarium and begin to convert harmful nitrogen compounds into less harmful forms.
In the world of fishkeeping, knowing if your tank is cycled is crucial for the health of your aquatic pets. Cycling refers to the establishment of beneficial bacteria in the tank, which convert harmful ammonia and nitrite into less toxic nitrates.
If you’re unsure whether your tank is cycled, there are a few telltale signs to look for. For instance, a clear lack of ammonia and nitrite, along with stable nitrate levels, often indicates a cycled tank. For more insights into this topic, refer to this comprehensive guide on how to know if a tank is cycled without testing.
The nitrogen cycle consists of two main stages: nitrification and denitrification. Nitrification is the process by which ammonia and nitrite are converted into nitrate. Denitrification is the process by which nitrate is converted into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere.
Benefits of Tank Cycling
Tank cycling is a crucial process that helps ensure the health and well-being of fish in an aquarium. It allows beneficial bacteria to establish, which play a vital role in maintaining water quality and preventing harmful conditions for fish.
During the cycling process, ammonia and nitrite levels rise as waste products from fish and other organic matter accumulate. Beneficial bacteria, including nitrifying bacteria, gradually colonize the tank and convert these toxic compounds into less harmful nitrates. The presence of these bacteria creates a balanced ecosystem that helps keep water parameters stable and suitable for fish life.
Importance of Beneficial Bacteria
Beneficial bacteria are essential for a healthy aquarium. They help to break down fish waste, uneaten food, and other organic matter that would otherwise pollute the water and create harmful conditions for fish.
- Nitrifying bacteriaconvert ammonia into nitrite and then into nitrate. These bacteria are crucial for removing toxic ammonia from the water.
- Denitrifying bacteriaconvert nitrate into nitrogen gas, which is released into the atmosphere. This process helps to keep nitrate levels in the tank low, which is important for fish health.
Duration of Tank Cycling
Tank cycling is a crucial process that establishes a stable and healthy ecosystem within your aquarium. It involves the development of beneficial bacteria that convert toxic ammonia and nitrite into less harmful nitrates. The duration of tank cycling varies depending on several factors.
Generally, it takes around 4-8 weeks for a tank to fully cycle. However, it’s important to note that this is just an estimate, and the actual time may vary based on the factors discussed below.
Factors Influencing Cycling Time
- Temperature:Higher temperatures accelerate bacterial growth, shortening the cycling time. Aim for a temperature range of 78-82°F (26-28°C).
- Filter:A strong filter with a large surface area provides more space for beneficial bacteria to colonize, speeding up the process.
- Water Changes:Regular water changes remove excess ammonia and nitrite, creating a more favorable environment for beneficial bacteria.
- Seeding:Adding beneficial bacteria from an established tank or using a commercial product can jumpstart the cycling process.
- Tank Size:Smaller tanks cycle faster than larger ones due to a higher concentration of waste products.
- Fish Load:Adding fish too early can overload the developing ecosystem, slowing down the cycling process.
Monitoring the Nitrogen Cycle: How Long To Let Fish Tank Cycle Before Adding Fish
To ensure a successful tank cycle, it is crucial to monitor the levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the water. This allows you to track the progress of the nitrogen cycle and make necessary adjustments.
Several methods are available for monitoring these parameters:
- Test Kits:Liquid or strip test kits can be used to measure the concentration of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the water. These kits provide accurate and reliable results, making them a popular choice for aquarium hobbyists.
- Electronic Monitors:Electronic monitors can continuously measure and display the levels of ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate in the water. While more expensive than test kits, these monitors offer real-time monitoring and can be particularly useful for large or complex aquariums.
During the cycling process, the ideal ranges for these parameters are as follows:
- Ammonia:0 ppm
- Nitrite:0 ppm
- Nitrate:Less than 20 ppm
Regular monitoring of these parameters allows you to identify any potential problems and take corrective action to ensure the health of your fish.
Signs of Completed Cycle
Determining the completion of the tank cycle is crucial before introducing fish to ensure their well-being. Several indicators signal the establishment of a healthy ecosystem:
Nitrite and Nitrate Levels
- Nitrite (NO2-):Should be 0 ppm. Elevated nitrite levels are toxic to fish.
- Nitrate (NO3-):Should be below 20 ppm. Nitrate is less toxic than nitrite but can still harm fish at high concentrations.
Ammonia Levels
- Should be 0 ppm. Ammonia is toxic to fish even at low concentrations.
Presence of Beneficial Bacteria
The presence of beneficial bacteria is essential for a healthy tank. These bacteria convert ammonia and nitrite into less toxic compounds. Indicators of their presence include:
- Cloudy water:During the initial stages of the cycle, the water may appear cloudy due to the presence of beneficial bacteria.
- Biofilm:A thin, slimy film may form on surfaces in the tank, indicating the presence of beneficial bacteria.
Adding Fish after Cycling
After completing the tank cycling process, it is essential to introduce fish gradually to avoid overwhelming the newly established ecosystem. Acclimating fish to their new environment is crucial for their well-being and survival.
Guidelines for Gradual Introduction
- Start by adding a small number of hardy fish, such as tetras or guppies.
- Monitor the water parameters closely for any signs of ammonia or nitrite spikes.
- If the water parameters remain stable, gradually add more fish over time.
- Avoid overcrowding the tank, as this can lead to stress and health issues for the fish.
Importance of Acclimation
Acclimating fish to their new environment involves gradually introducing them to the tank water’s temperature, pH, and other parameters. This process minimizes stress and reduces the risk of shock or death.
- Float the fish in a sealed bag in the tank water for 15-30 minutes.
- Gradually add small amounts of tank water to the bag over the next hour.
- Once the bag is mostly filled with tank water, release the fish into the tank.
Troubleshooting Tank Cycling Issues
Tank cycling is a crucial process that ensures the establishment of a healthy and stable aquatic environment for fish. However, certain problems can arise during this process, potentially delaying or even hindering its completion.Common issues that may occur during tank cycling include:
Slow Cycling
* Cause:Insufficient beneficial bacteria growth due to factors such as low temperatures, lack of ammonia source, or improper pH levels.
Solution
Increase water temperature to 78-82°F (26-28°C), provide an ammonia source (e.g., fish food, pure ammonia), and adjust pH to 7.2-7.6.
Nitrite Spike
* Cause:Accumulation of nitrite-producing bacteria before the growth of nitrate-producing bacteria.
Solution
Continue water changes to reduce nitrite levels and add live bacteria supplements to accelerate the growth of nitrate-producing bacteria.
If you’re an avid cyclist, you know the importance of finding the perfect pair of bike shorts. Not only do they provide comfort during long rides, but they also protect your delicate areas from chafing and saddle sores. When it comes to fit, bike shorts should be snug but not too tight, allowing for a full range of motion without bunching or riding up.
For more detailed guidance, check out this article on how bike shorts should fit.
Stalled Cycle, How long to let fish tank cycle before adding fish
* Cause:Sudden changes in water chemistry, overfeeding, or insufficient filtration.
Solution
Perform partial water changes, reduce feeding frequency, and ensure adequate filtration capacity.
High Ammonia or Nitrite Levels
* Cause:Overfeeding, overcrowding, or malfunctioning filtration system.
Solution
Perform immediate water changes to dilute the levels, reduce feeding, and inspect and clean the filtration system.
Cloudy Water
* Cause:Bacterial bloom or presence of suspended particles.
Solution
Perform water changes, use a clarifying agent, and improve filtration.
Additional Tips
* Monitor water parameters regularly using test kits.
- Avoid using antibacterial medications or cleaning products that can harm beneficial bacteria.
- Be patient and allow ample time for the cycling process to complete.
- Seek professional advice from an experienced aquarist or aquatic veterinarian if persistent problems arise.
Special Considerations for Different Tank Types
Cycling requirements and procedures may vary depending on the type of aquarium.
Freshwater Tanks
* Cycling typically takes 4-6 weeks.
- Establish a stable bacterial colony by adding an ammonia source, such as fish food or pure ammonia.
- Monitor ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels regularly.
Saltwater Tanks
* Cycling can take longer, up to 8-12 weeks.
- Requires a more complex ecosystem, including nitrifying bacteria and algae.
- Introduce live rock or other biological filters to accelerate the process.
Planted Tanks
* Plants utilize nitrates as nutrients, reducing their accumulation.
- Cycle for a shorter period, around 2-4 weeks.
- Ensure adequate lighting and CO2 levels to support plant growth.
Using Beneficial Bacteria Products

Commercial beneficial bacteria products are available to help accelerate the nitrogen cycle in a fish tank. These products contain live bacteria that can be added to the tank to supplement the natural bacteria that develop during cycling.
Using beneficial bacteria products can have several advantages. First, it can help to speed up the cycling process, allowing you to add fish to your tank sooner. Second, it can help to prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria, which can lead to fish health problems.
Third, it can help to improve the overall water quality in your tank.
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to using beneficial bacteria products. First, they can be expensive. Second, they may not always be effective, especially if the tank is not properly maintained. Third, they can introduce harmful bacteria into the tank if they are not used properly.
Pros of Using Beneficial Bacteria Products
- Can help to speed up the cycling process
- Can help to prevent the buildup of harmful bacteria
- Can help to improve the overall water quality in your tank
Cons of Using Beneficial Bacteria Products
- Can be expensive
- May not always be effective
- Can introduce harmful bacteria into the tank if not used properly
Advanced Cycling Techniques
Advanced cycling techniques can accelerate the establishment of a stable nitrogen cycle in a new aquarium. These methods involve introducing beneficial bacteria from an established tank or using commercial products containing these bacteria.
Media Seeding
Media seeding involves transferring filter media or substrate from an established aquarium to a new one. This introduces beneficial bacteria that can colonize the new filter and substrate, jump-starting the nitrogen cycle. It’s a quick and effective way to cycle a tank in a few days or weeks.
Bottled Bacteria
Commercial products containing live beneficial bacteria can also be used to cycle a tank. These products are typically added to the aquarium water and contain a blend of bacteria strains that help establish the nitrogen cycle. While convenient, they may not be as effective as media seeding and can take longer to establish a stable cycle.
Closing Notes
In summary, cycling a fish tank before adding fish is a crucial step in creating a healthy and thriving aquatic environment. By allowing the tank to go through the nitrogen cycle and establish a stable bacterial colony, you can ensure the well-being of your fish and prevent potential health issues.
Remember to monitor water parameters closely, be patient, and gradually introduce fish to your tank to avoid overwhelming the biological system.
FAQ
How long does it take to cycle a fish tank?
The time it takes to cycle a fish tank can vary depending on factors such as tank size, temperature, and the presence of live plants. However, a general timeline is around 4-8 weeks.
What are the signs that my fish tank is cycled?
Indicators of a completed cycle include stable ammonia and nitrite levels at 0 ppm, and nitrate levels below 20 ppm. Additionally, the presence of beneficial bacteria colonies on surfaces within the tank is a good sign.
Can I add fish to my tank while it’s cycling?
It’s not recommended to add fish during the cycling process, as the unstable water parameters can harm or even kill them. Wait until the cycle is complete and water parameters are stable before introducing fish.
