Cycling, a popular form of exercise, offers numerous health benefits. One key aspect of cycling is the number of calories burned, which can vary depending on several factors. This article delves into the topic of how many calories burned cycling a mile, providing insights into calorie expenditure, variables affecting calorie burn, and strategies for optimizing calorie burn while cycling.
Calorie Expenditure: How Many Calories Burned Cycling A Mile
Cycling, a popular cardiovascular exercise, burns calories and contributes to weight management and overall fitness. Calorie expenditure during cycling depends on various factors, including intensity, duration, and individual characteristics.
Formula for Calorie Burn
The most common formula used to estimate calorie burn while cycling is the MET formula, which considers the metabolic equivalent of task (MET) value for cycling and multiplies it by body weight in kilograms and duration in minutes.
MET x Body weight (kg) x Duration (min) / 60 = Calories burned
The MET value for cycling varies depending on intensity, ranging from 6 METs for moderate cycling to 8 METs for vigorous cycling.
Factors Influencing Calorie Expenditure
Several factors influence calorie expenditure during cycling, including:
- Intensity:Higher intensity cycling burns more calories per minute compared to lower intensity cycling.
- Duration:The longer the duration of cycling, the more calories are burned.
- Weight:Individuals with higher body weight burn more calories while cycling compared to those with lower body weight.
- Fitness level:Fitter individuals burn calories more efficiently, resulting in fewer calories burned per minute compared to less fit individuals.
- Terrain:Cycling on hills or uneven terrain requires more effort and burns more calories compared to cycling on flat surfaces.
- Wind resistance:Cycling against the wind increases calorie expenditure compared to cycling with the wind.
Variables Affecting Calorie Burn
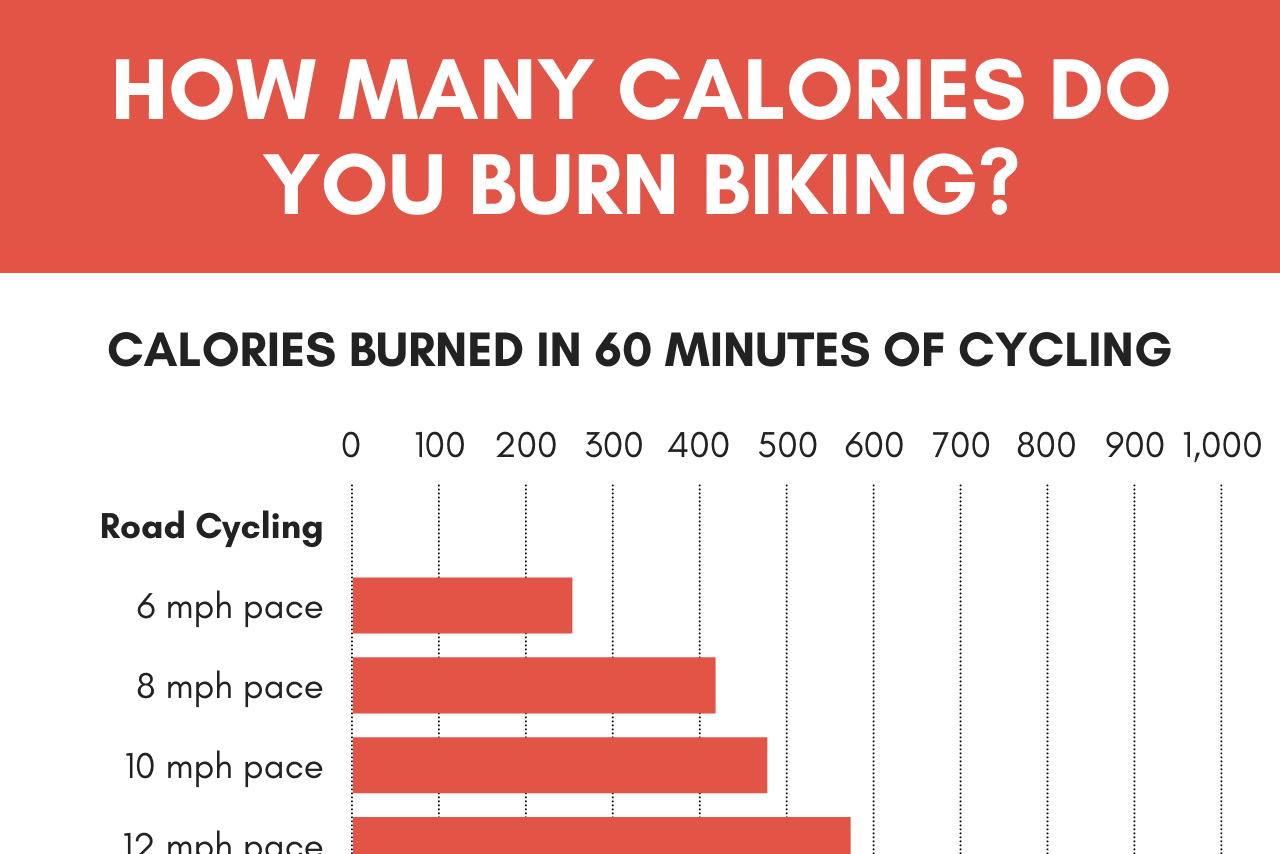
The number of calories burned while cycling depends on several factors, including intensity, duration, and weight.
Intensity
The intensity of your cycling workout significantly impacts calorie burn. Higher-intensity workouts, such as sprints or hill climbs, burn more calories than lower-intensity workouts, such as leisurely rides.
Duration
The longer you cycle, the more calories you will burn. However, the rate at which you burn calories decreases over time as your body becomes more efficient at the activity.
Weight
Heavier individuals burn more calories while cycling than lighter individuals. This is because they have to work harder to move their body weight.
Comparison with Other Activities
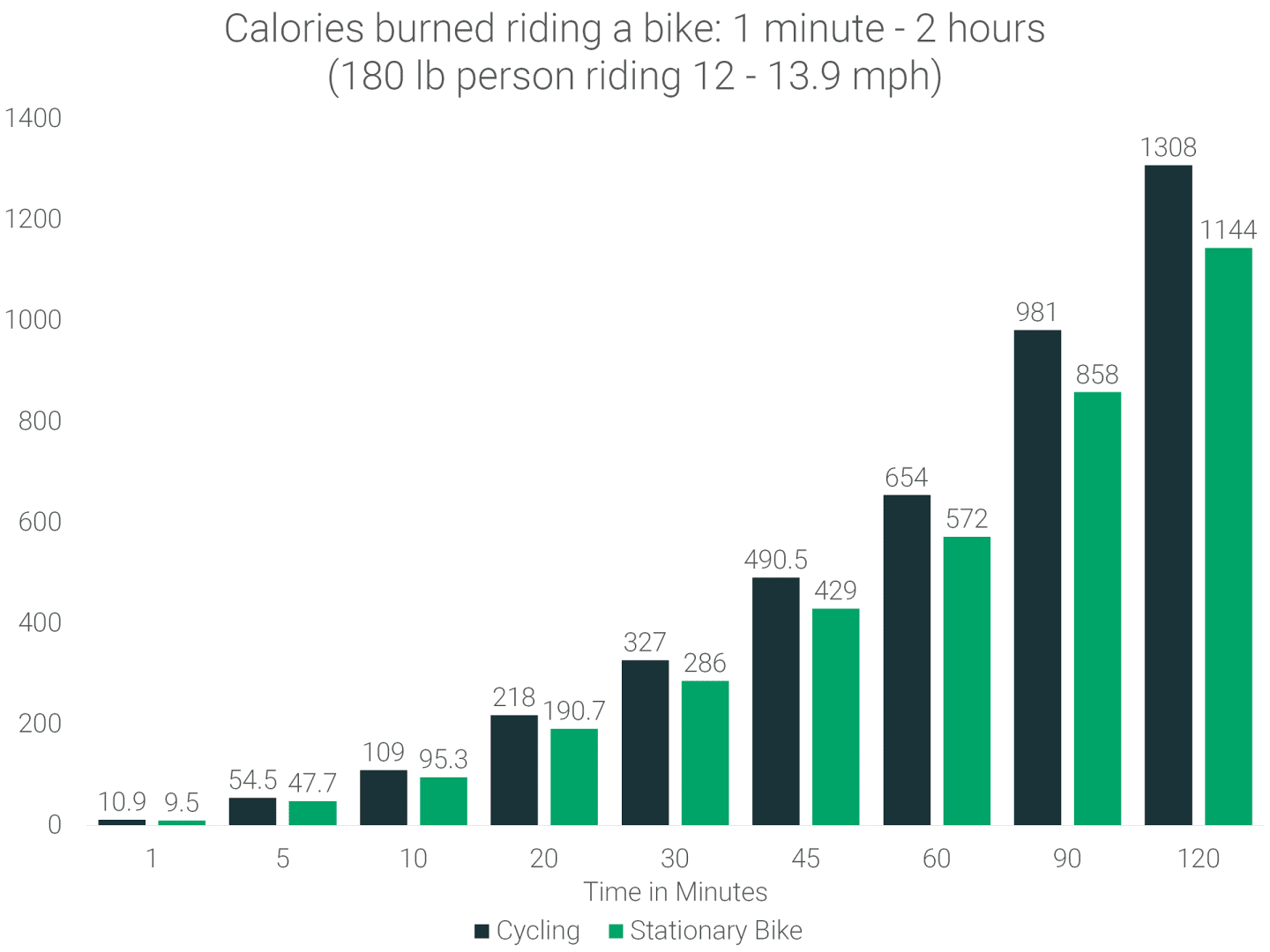
Cycling offers a moderate to vigorous workout, but how does it compare to other popular exercises in terms of calorie burn? Let’s delve into a table that provides insights into the calorie expenditure per mile for cycling and other activities.
Calorie Burn per Mile Comparison
| Exercise | Calories Burned per Mile ||—|—|| Cycling (moderate pace) | 300-400 || Cycling (vigorous pace) | 400-500 || Running | 500-600 || Swimming | 400-500 || Elliptical training | 350-450 |Cycling falls within the moderate to vigorous range of calorie expenditure, making it a good choice for those seeking a balanced workout.
While running typically burns more calories per mile, cycling offers a lower-impact option that is easier on the joints.Cycling also provides a consistent, full-body workout, engaging multiple muscle groups. The continuous motion of pedaling promotes cardiovascular fitness and endurance. Compared to elliptical training, cycling may burn slightly more calories and offer a more challenging workout.
Swimming, while an excellent full-body exercise, may have a slightly lower calorie burn per mile than cycling at a moderate pace.
Calorie Burn Optimization
Maximizing calorie burn while cycling requires a combination of strategies that target both intensity and efficiency. This includes implementing interval training, tackling hill climbs, and maintaining proper cycling form. Additionally, staying hydrated and fueling your body with appropriate nutrition are crucial for optimizing calorie expenditure.
Interval Training
Interval training involves alternating between high-intensity bursts and recovery periods. This method elevates your heart rate and metabolism, leading to increased calorie burn during and after the workout. Incorporate intervals into your cycling routine by alternating between sprints and steady-state cycling.
Hill Climbing
Cycling uphill requires greater effort and engages more muscle groups, resulting in a higher calorie burn. Seek out hills in your cycling routes and challenge yourself with ascents. The added resistance will push your limits and enhance calorie expenditure.
Proper Cycling Form
Maintaining proper cycling form not only improves comfort and efficiency but also contributes to calorie burn. Ensure your saddle is at the correct height, allowing for a slight bend in your knee at the bottom of the pedal stroke. Engage your core muscles and keep your back straight to maximize power output and energy expenditure.
Hydration and Nutrition
Staying adequately hydrated is essential for overall health and performance. Dehydration can impair metabolism and reduce calorie burn. Drink plenty of water before, during, and after your cycling workouts. Additionally, fueling your body with a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats supports sustained energy levels and optimizes calorie expenditure.
Calorie Burn Monitoring
Tracking calorie burn during cycling is crucial for monitoring progress and optimizing training. Various devices are available to help cyclists accurately measure their energy expenditure.
Fitness Trackers, How many calories burned cycling a mile
Fitness trackers worn on the wrist or arm use accelerometers to estimate calorie burn based on movement and heart rate. They provide real-time data and allow for continuous tracking throughout the ride.
Accuracy:Moderate. Fitness trackers are generally less accurate than other methods but can provide a reasonable estimate for casual cyclists.
Heart Rate Monitors
Heart rate monitors measure heart rate using a chest strap or wrist-worn sensor. Calorie burn is calculated based on heart rate data and personal information like age, weight, and gender.
If you’re looking for a challenging and scenic cycling experience, consider the Five Borough Bike Tour. The route covers over 40 miles, taking you through all five boroughs of New York City. To prepare for the ride, it’s important to know how long the Five Borough Bike Tour will take and how to warm up after an ice bath, if needed.
With proper planning, you can ensure a safe and enjoyable cycling adventure.
Accuracy:High. Heart rate monitors provide a more precise estimate of calorie burn compared to fitness trackers, especially for higher-intensity workouts.
Cycling Computers
Cycling computers mount on the handlebars and use GPS and power meters to calculate calorie burn. They provide detailed metrics like distance, speed, and power output.
Accuracy:Highest. Cycling computers offer the most accurate calorie burn estimates, especially when paired with a power meter that measures the force applied to the pedals.
Limitations:
- All devices can be affected by factors like individual metabolism, fitness level, and environmental conditions.
- Fitness trackers and heart rate monitors may struggle to accurately measure calorie burn during interval training or hill climbs.
Interpreting Data:
If you’re planning on taking the Five Borough Bike Tour , it’s important to know that the distance is about 40 miles. That’s a long ride, so make sure you’re prepared. If you’re not used to riding that far, you might want to start training a few weeks in advance.
And don’t forget to warm up properly before you start your ride. There are a few different ways to warm up, but one of the most effective is to take a warm bath or shower. This will help to increase your blood flow and get your muscles ready for the ride.
- Use calorie burn data to set realistic fitness goals and track progress.
- Compare calorie burn across different rides to identify areas for improvement.
- Combine calorie burn data with other metrics like heart rate and power output for a comprehensive understanding of workout intensity.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, the number of calories burned cycling a mile depends on various factors such as intensity, duration, weight, and cycling efficiency. By understanding these factors and implementing strategies like interval training, hill climbing, and proper cycling form, individuals can maximize their calorie burn while enjoying the many benefits of cycling.
Essential Questionnaire
How can I track my calorie burn while cycling?
Fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, and cycling computers are effective tools for tracking calorie burn during cycling.
What is the most efficient way to burn calories while cycling?
Interval training, hill climbing, and maintaining proper cycling form are effective strategies for maximizing calorie burn while cycling.
How does body weight affect calorie burn while cycling?
Individuals with higher body weight tend to burn more calories while cycling compared to those with lower body weight.
