How much does a racing bike weigh? This seemingly simple question delves into a realm of intricate design, material science, and performance optimization. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the factors that determine the weight of a racing bike, exploring the trade-offs and innovations that shape these high-performance machines.
From the materials used in the frame to the components that make up the drivetrain, every element contributes to the overall weight of a racing bike. Understanding these factors empowers cyclists to make informed choices that align with their riding style and performance goals.
Materials and Components
The materials and components used in the construction of a racing bike play a crucial role in determining its overall weight. Different materials offer varying levels of strength, stiffness, and weight, and the choice of components can significantly impact the bike’s performance and handling characteristics.
Frame Materials
The frame is the backbone of a racing bike, and the material used for its construction has a significant impact on the bike’s weight. The most common frame materials include:
- Steel:Steel frames are relatively heavy and less stiff compared to other materials, but they are also durable and affordable.
- Aluminum:Aluminum frames offer a good balance of weight, stiffness, and durability. They are lighter than steel frames but more expensive.
- Carbon fiber:Carbon fiber frames are the lightest and stiffest, but they are also the most expensive. They offer excellent performance and handling characteristics.
- Titanium:Titanium frames are lightweight and very strong, but they are also very expensive. They are often used in high-end racing bikes.
Components
In addition to the frame, the components used on a racing bike also contribute to its overall weight. These components include:
- Gears:The gears on a racing bike are responsible for transferring power from the pedals to the wheels. The number of gears and the materials used in their construction can impact the bike’s weight.
- Brakes:The brakes on a racing bike are used to slow down or stop the bike. The type of brakes used and the materials used in their construction can impact the bike’s weight.
- Wheels:The wheels on a racing bike are responsible for supporting the bike and rolling it along the ground. The size, materials, and construction of the wheels can impact the bike’s weight.
Frame Design and Geometry
Frame design plays a crucial role in determining a racing bike’s weight. The shape, size, and angles of the frame affect weight distribution and overall performance.
Lighter frames are achieved by using thinner tubes, but this can compromise structural integrity. Therefore, frame designers must strike a balance between weight reduction and ensuring the bike can withstand the rigors of racing.
It’s important to replace your motorcycle helmet regularly for safety reasons. How often should you change your motorcycle helmet depends on several factors, including the frequency of use, the climate you ride in, and any accidents or damage the helmet has sustained.
Tube Shape and Size
The shape and size of the frame tubes influence both weight and strength. Round tubes are the most common, but they are not as aerodynamic as airfoil-shaped tubes. Airfoil tubes reduce drag, but they are also more difficult to manufacture and can be heavier.
The size of the tubes also affects weight. Thinner tubes are lighter, but they can be less stiff and more prone to damage. Thicker tubes are stronger and stiffer, but they are also heavier.
After a hysterectomy, tracking your cycle can be challenging. However, there are still ways to track your cycle after hysterectomy. By monitoring your physical symptoms, such as mood changes, sleep patterns, and vaginal discharge, you can gain insights into your hormonal fluctuations and predict your menstrual cycle.
Frame Angles
The angles of the frame also affect weight distribution. A steeper head tube angle makes the bike more responsive, but it can also make it less stable at high speeds. A slacker head tube angle provides more stability, but it can make the bike less maneuverable.
The seat tube angle also affects weight distribution. A steeper seat tube angle puts the rider in a more aggressive position, which can be more efficient for racing. A slacker seat tube angle provides a more comfortable riding position, but it can be less efficient.
Weight Categories and Standards
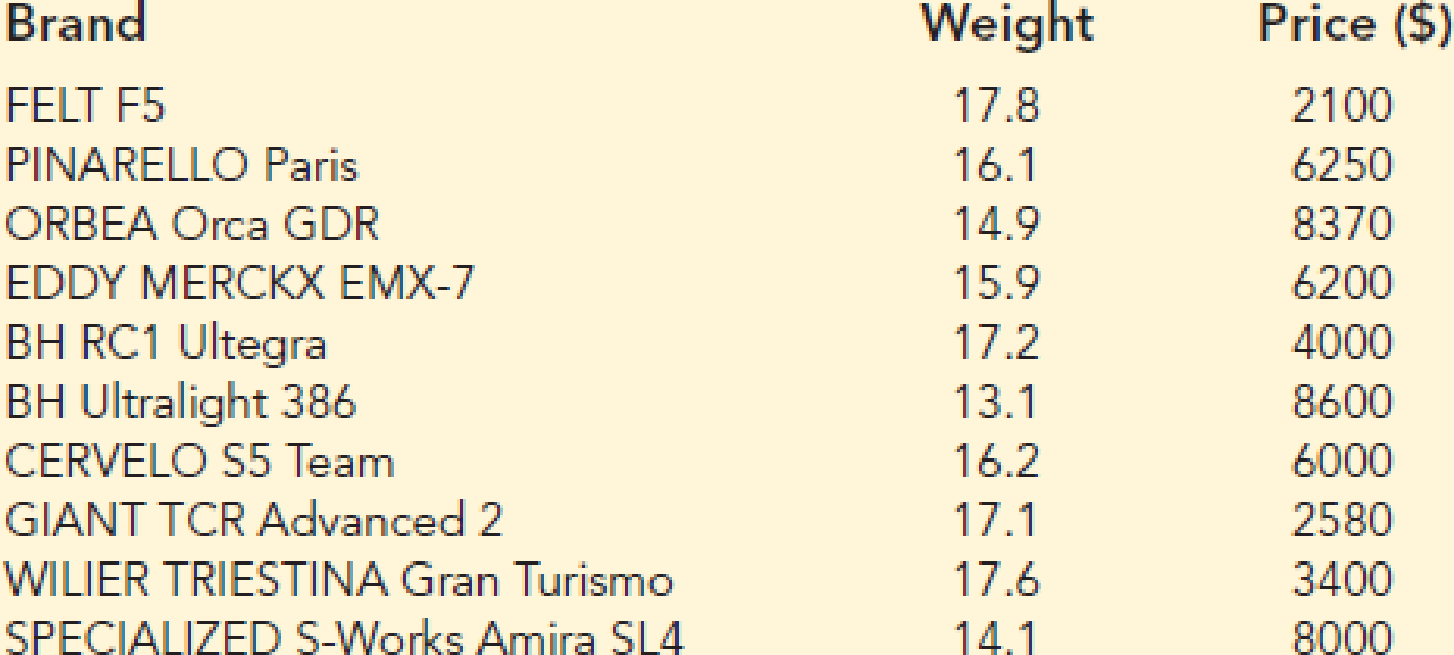
Racing bikes are classified into various weight categories based on their overall weight and specific components used in their construction. These categories help riders choose bikes that align with their performance goals, riding style, and terrain preferences.
The factors considered when classifying bikes into weight categories include the frame material, component selection (wheels, tires, handlebars, etc.), and overall bike size. Lighter bikes generally offer better acceleration and climbing abilities, while heavier bikes may provide increased stability and durability.
Weight Categories
The following table Artikels the different weight categories for racing bikes and their corresponding standards:
| Category | Weight Range (kg) |
|---|---|
| Superlight | Under 6.8 |
| Lightweight | 6.8
|
| Midweight | 7.5
|
| Heavyweight | Over 8.5 |
Weight Optimization Techniques
In the pursuit of performance, reducing the weight of a racing bike is a critical aspect. Engineers and designers have developed innovative methods and technologies to minimize bike weight while maintaining structural integrity and ride quality.
The balance between weight reduction and performance considerations is crucial. While a lighter bike can enhance acceleration, climbing ability, and overall speed, excessive weight reduction can compromise durability, handling, and safety.
Materials and Manufacturing
- Carbon Fiber:Carbon fiber frames are lightweight, stiff, and strong, making them the preferred choice for high-end racing bikes.
- Titanium:Titanium is another lightweight and durable material used in frame construction, offering a balance of strength and weight.
- Hydroforming:Hydroforming is a process that uses pressurized water to shape metal tubes, allowing for complex shapes and weight reduction.
Component Design
- Lightweight Components:Manufacturers use lightweight materials like carbon fiber and titanium for components such as handlebars, stems, seatposts, and wheels.
- Integrated Components:Integrating components, such as seatposts and brakes, into the frame can reduce weight and improve aerodynamics.
- Tubeless Tires:Tubeless tires eliminate the need for inner tubes, saving weight and reducing rolling resistance.
Aerodynamic Optimization
- Aero Frames:Frames are designed with aerodynamic shapes to reduce wind resistance and improve speed.
- Integrated Fairings:Fairings around the fork and rear wheel can further reduce drag.
- Dropped Seat Stays:Dropped seat stays allow for a more aerodynamic position by bringing the saddle closer to the rear wheel.
Impact on Performance and Handling
Weight reduction is a key factor in enhancing the performance and handling of racing bikes. A lighter bike accelerates faster, climbs more efficiently, and maneuvers with greater agility.
The optimal weight range for different types of racing varies depending on the demands of the discipline. For example, time trial bikes prioritize aerodynamics and speed, while mountain bikes require durability and stability on rough terrain.
Acceleration, How much does a racing bike weigh
A lighter bike requires less force to accelerate, resulting in faster starts and quicker responses to changes in pace.
Climbing Ability
On climbs, a lighter bike reduces the force required to lift it against gravity, making ascents easier and more efficient.
Handling
A lighter bike is easier to maneuver, allowing for quicker cornering, better balance, and improved control at high speeds.
Epilogue: How Much Does A Racing Bike Weigh
Ultimately, the weight of a racing bike is a delicate balance between performance, handling, and durability. Whether you’re a seasoned racer or an aspiring enthusiast, this guide has provided insights into the intricacies of bike weight and its impact on your riding experience.
By considering the factors discussed, you can make informed decisions that will optimize your bike’s performance and enhance your cycling journey.
Q&A
What materials are commonly used in racing bike frames?
Carbon fiber, aluminum, titanium, and steel are the primary materials used in racing bike frames, each offering unique combinations of weight, stiffness, and durability.
How do different components affect the weight of a racing bike?
Components such as the drivetrain, wheels, brakes, and handlebars all contribute to the overall weight of the bike. Lighter components can significantly reduce the bike’s weight, but they may also impact durability and performance.
What is the optimal weight range for a racing bike?
The optimal weight range for a racing bike depends on the type of racing and the rider’s individual preferences. Generally, lighter bikes are more efficient on climbs, while heavier bikes may provide better stability and handling on descents.
