How often should a heat pump cycle on and off? It’s a question that can have a big impact on your energy bills, comfort levels, and the lifespan of your equipment. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the factors that affect heat pump cycling frequency and provide tips for optimizing performance.
From understanding the impact on energy efficiency to troubleshooting common issues, we’ve got you covered.
Energy Efficiency
The frequency of a heat pump’s cycling can significantly impact its energy consumption. When a heat pump cycles on and off frequently, it uses more energy than when it operates continuously. This is because the compressor, which is the main energy-consuming component of a heat pump, must work harder to bring the system up to temperature each time it cycles on.
Reducing Cycling
There are several ways to reduce the cycling of a heat pump, including:
- Proper sizing:A heat pump that is properly sized for the space it is heating or cooling will not have to cycle as often to maintain the desired temperature.
- Regular maintenance:A well-maintained heat pump will operate more efficiently and cycle less often.
- Using a programmable thermostat:A programmable thermostat can be used to set the temperature of the home to a lower setting during times when the home is unoccupied or when the occupants are sleeping. This can help to reduce the frequency of cycling.
Compressor Lifespan
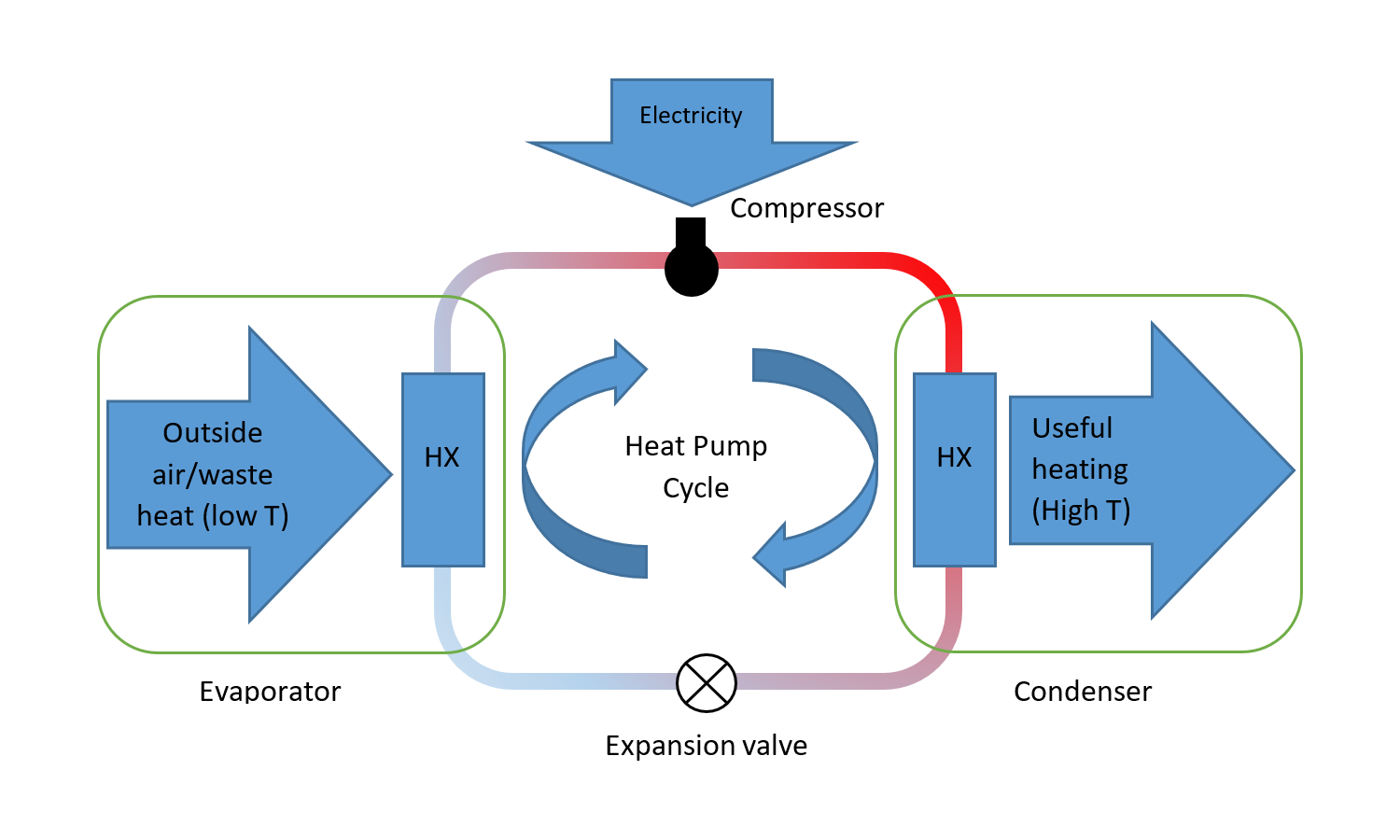
Heat pumps rely on compressors to circulate refrigerant, a vital process for heating and cooling. However, excessive cycling can strain the compressor, leading to premature wear and reduced lifespan.
Relationship between Cycling Frequency and Compressor Wear
When a heat pump cycles on and off frequently, the compressor is subjected to repeated starting and stopping stresses. These sudden changes in pressure and temperature can cause wear and tear on the compressor’s components, such as the bearings, valves, and piston rings.
Over time, this can lead to decreased efficiency, increased noise, and eventual failure.
Effects of Excessive Cycling
Research indicates that heat pumps that cycle excessively experience a significantly shorter lifespan compared to those that cycle less frequently. Studies have shown that compressors subjected to high cycling rates can fail up to 50% sooner than those operating at normal cycling frequencies.
Comfort Levels
The frequency of a heat pump’s cycling can significantly impact the stability of indoor temperatures. When the system cycles frequently, it can lead to temperature fluctuations, making it challenging to maintain a comfortable living environment. On the other hand, if the cycling is too infrequent, the system may not be able to respond quickly enough to changes in temperature, resulting in discomfort.
Optimizing Cycling for Comfort
To optimize the cycling of a heat pump for maximum comfort, consider the following tips:
- Set the thermostat to a consistent temperature:Avoid frequent adjustments to the thermostat, as this can trigger unnecessary cycling. Choose a temperature that is comfortable and maintain it throughout the day.
- Use a programmable thermostat:With a programmable thermostat, you can set different temperatures for different times of the day. This allows you to adjust the temperature when you are away or sleeping, reducing the need for frequent cycling.
- Check the system’s airflow:Ensure that the air filters are clean and that there are no obstructions blocking the airflow. Proper airflow helps the system operate efficiently and reduces the likelihood of frequent cycling.
- Consider a larger heat pump:If the heat pump is too small for the space it is heating or cooling, it will have to work harder and cycle more frequently. Upgrading to a larger system can improve comfort and reduce cycling.
System Sizing
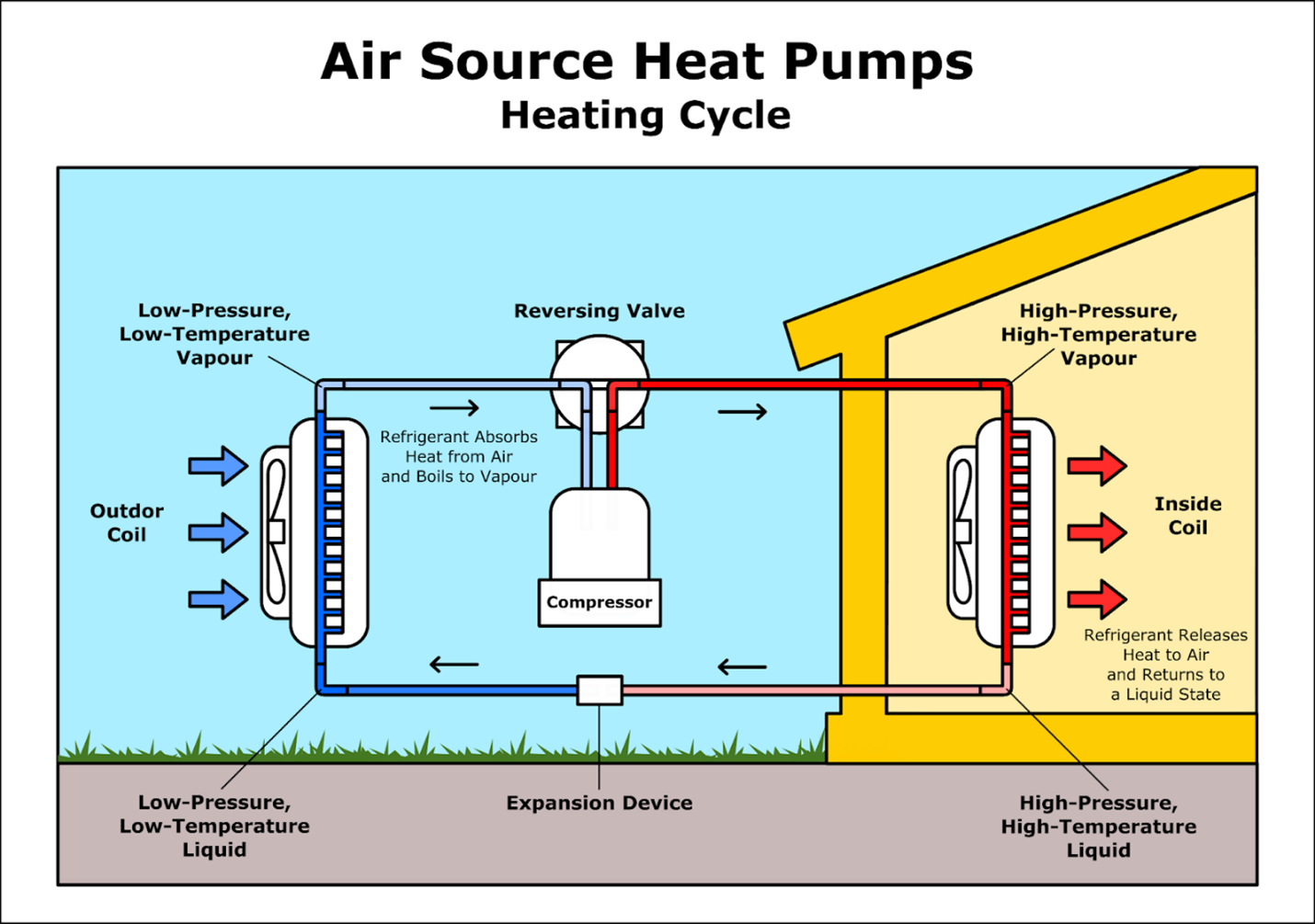
Proper system sizing is crucial for determining the cycling frequency of a heat pump. An appropriately sized heat pump will maintain a comfortable indoor temperature without excessive cycling.
When selecting the right size for a heat pump, several factors must be considered:
Heating and Cooling Loads
- The size of the home and the number of rooms that need heating or cooling.
- The level of insulation in the home, which affects the amount of heat loss or gain.
- The number of windows and their orientation, as well as the amount of sunlight the home receives.
- The climate zone where the home is located, which determines the heating and cooling requirements.
Equipment Efficiency, How often should a heat pump cycle on and off
The efficiency of the heat pump, measured by its SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) or HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor), also plays a role. A higher efficiency rating indicates that the heat pump can move more heat with less energy, reducing the number of cycles needed to maintain the desired temperature.
Proper Installation
Professional installation is essential to ensure that the heat pump is properly sized and installed. An improperly sized or installed heat pump can lead to excessive cycling, reduced efficiency, and premature failure.
Environmental Conditions
The cycling patterns of a heat pump are influenced by outdoor temperature and humidity levels. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can affect the efficiency and lifespan of the unit. Additionally, high humidity levels can lead to increased cycling, which can shorten the lifespan of the compressor.
Outdoor Temperature
In general, heat pumps are less efficient at extreme temperatures. When the outdoor temperature is very high, the heat pump has to work harder to cool the home, which can lead to increased cycling. Similarly, when the outdoor temperature is very low, the heat pump has to work harder to heat the home, which can also lead to increased cycling.
| Outdoor Temperature | Effect on Cycling |
|---|---|
| Very high | Increased cycling |
| Very low | Increased cycling |
| Moderate | Normal cycling |
Outdoor Humidity
High humidity levels can also affect the cycling patterns of a heat pump. When the outdoor humidity is high, the heat pump has to work harder to remove moisture from the air, which can lead to increased cycling. This can shorten the lifespan of the compressor.
| Outdoor Humidity | Effect on Cycling |
|---|---|
| High | Increased cycling |
| Low | Normal cycling |
Troubleshooting
Excessive cycling of a heat pump can be a sign of underlying issues that need to be addressed to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the system. Identifying the common causes of excessive cycling and following a step-by-step troubleshooting process can help resolve these issues effectively.
Below are some common causes of excessive cycling and steps to troubleshoot and resolve them:
Common Causes and Troubleshooting Steps
- Oversized Heat Pump:A heat pump that is too large for the space it is heating or cooling will cycle on and off frequently in an attempt to maintain the desired temperature. The solution is to replace the oversized heat pump with a properly sized unit.
- Dirty Air Filter:A dirty air filter can restrict airflow, causing the heat pump to work harder and cycle more frequently. The solution is to replace the dirty air filter with a clean one.
- Refrigerant Leaks:Refrigerant leaks can reduce the efficiency of the heat pump, causing it to cycle more frequently to maintain the desired temperature. The solution is to have the refrigerant leak repaired by a qualified technician.
- Faulty Thermostat:A faulty thermostat can send incorrect signals to the heat pump, causing it to cycle on and off too frequently. The solution is to replace the faulty thermostat with a new one.
- Electrical Problems:Electrical problems, such as loose connections or faulty wiring, can cause the heat pump to cycle on and off unexpectedly. The solution is to have an electrician inspect and repair any electrical problems.
Last Recap
By understanding the factors that influence heat pump cycling frequency, you can optimize your system’s performance, save energy, and extend its lifespan. Remember, regular maintenance and professional inspections are crucial for ensuring your heat pump operates efficiently and reliably for years to come.
Essential FAQs: How Often Should A Heat Pump Cycle On And Off
How can I reduce the cycling frequency of my heat pump?
Proper system sizing, regular maintenance, and addressing any underlying issues can help reduce cycling frequency.
What are the signs of excessive heat pump cycling?
Short cycles, frequent on/off cycles, and inconsistent indoor temperatures can indicate excessive cycling.
How does outdoor temperature affect heat pump cycling?
Extreme temperatures can increase cycling frequency as the heat pump works harder to maintain the desired indoor temperature.
